Beneficial Effect of 7-O-Galloyl-D-sedoheptulose, a Polyphenol Isolated from Corni Fructus, against Diabetes-Induced Alterations in Kidney and Adipose Tissue of Type 2 Diabetic db/db Mice
- PMID: 24348717
- PMCID: PMC3853307
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/736856
Beneficial Effect of 7-O-Galloyl-D-sedoheptulose, a Polyphenol Isolated from Corni Fructus, against Diabetes-Induced Alterations in Kidney and Adipose Tissue of Type 2 Diabetic db/db Mice
Abstract
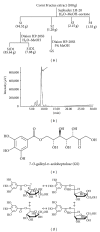
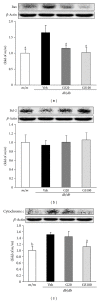
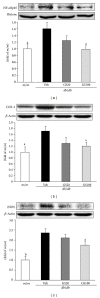
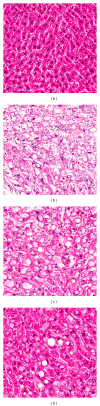
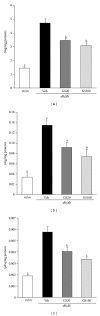
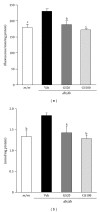
Traditional medicines are being focused on as possible treatments for diabetes and its complications because of their negligible toxic and/or side effects. In line with this, our group has reported that Corni Fructus, a traditional medicine considered exhibiting beneficial effects on liver and kidney functions, possessed an antidiabetic effect via ameliorating glucose-mediated metabolic disorders. To add to these findings, we screened the iridoid glycoside fraction containing morroniside and loganin, and low molecular weight polyphenol fraction containing 7-O-galloyl-d-sedoheptulose (GS) from Corni Fructus. To our knowledge, GS is a compound only detected in Corni Fructus, and its biological activity has been poorly understood until now. For these reasons, we examined whether GS has an ameliorative effect on diabetic changes using type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Our findings suggest that GS has a beneficial effect on the pathological state of the serum, kidney, and adipose tissue related to diabetic damage.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bioactive constituents of Corni Fructus: The therapeutic use of morroniside, loganin, and 7-O-galloyl-D-sedoheptulose as renoprotective agents in type 2 diabetes.Drug Discov Ther. 2010 Aug;4(4):223-34. Drug Discov Ther. 2010. PMID: 22491205
-
Polyphenol isolated from Corni Fructus, 7-O-galloyl-D-sedoheptulose, modulates advanced glycation endproduct-related pathway in type 2 diabetic db/db mice.Arch Pharm Res. 2015 Jun;38(6):1270-80. doi: 10.1007/s12272-014-0457-7. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Arch Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25079767
-
Evaluation of 7-O-galloyl-D-sedoheptulose, isolated from Corni Fructus, in the adipose tissue of type 2 diabetic db/db mice.Fitoterapia. 2013 Sep;89:131-42. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2013.03.026. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Fitoterapia. 2013. PMID: 23567861
-
A systematic review on anti-diabetic action of 7-O-galloyl-D-sedoheptulose, a polyphenol from Corni Fructus, in type 2 diabetic mice with hepatic and pancreatic damage.Drug Discov Ther. 2023 Jul 12;17(3):151-156. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2022.01097. Epub 2023 May 27. Drug Discov Ther. 2023. PMID: 37245985
-
Oligonol, a low-molecular-weight polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, attenuates gluco-lipotoxicity-mediated renal disorder in type 2 diabetic db/db mice.Drug Discov Ther. 2015 Feb;9(1):13-22. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2015.01003. Drug Discov Ther. 2015. PMID: 25788048 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Study of Crude and Wine-Processing Corni Fructus on Chemical Composition and Antidiabetic Effects.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Dec 2;2019:3986964. doi: 10.1155/2019/3986964. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31885645 Free PMC article.
-
Corni Fructus attenuates testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia by suppressing 5α-reductase and androgen receptor expression in rats.Nutr Res Pract. 2018 Oct;12(5):378-386. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2018.12.5.378. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Nutr Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30323905 Free PMC article.
-
Cornuside Alleviates Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Testicular Damage by Modulating the Gut Microbiota.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 30;2021:5301942. doi: 10.1155/2021/5301942. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34497657 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Bushen-Jiangya granules on blood pressure and pharmacogenomic evaluation in low-to-medium-risk hypertensive patients: study protocol for a randomized double-blind controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Jan 15;23(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-05999-2. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35033168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ, Van Haeften TW. Type 2 diabetes: principles of pathogenesis and therapy. The Lancet. 2005;365(9467):1333–1346. - PubMed
-
- Brownlee M, Cerami A, Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. New England Journal of Medicine. 1988;318(20):1315–1321. - PubMed
-
- Singh R, Barden A, Mori T, Beilin L. Advanced glycation end-products: a review. Diabetologia. 2001;44(2):129–146. - PubMed
-
- Inoguchi T, Battan R, Handler E, Sportsman JR, Heath W, King GL. Preferential elevation of protein kinase C isoform βII and diacylglycerol levels in the aorta and heart of diabetic rats: differential reversibility to glycemic control by islet cell transplantation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1992;89(22):11059–11063. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

