Grape seed extract attenuates arsenic-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 24348802
- PMCID: PMC3861237
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.1381
Grape seed extract attenuates arsenic-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
Abstract
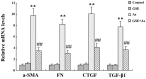
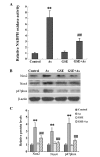
Oxidative stress is a recognized factor in nephrotoxicity induced by chronic exposure to inorganic arsenic (As). Grape seed extract (GSE) possesses antioxidant properties. The present study was designed to evaluate the beneficial effects of GSE against arsenic-induced renal injury. Healthy, male Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to As in drinking water (30 ppm) with or without GSE (100 mg/kg) for 12 months. The serum proinflammatory cytokine levels and mRNA expression levels of fibrogenic markers in the renal tissues were evaluated using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and quantitative polymerase chain reaction, respectively. The protein expression levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) subunits, transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and phosphorylated Smad2/3 (pSmad2/3) were assessed using western blot analysis. The results demonstrated that cotreatment with GSE significantly improved renal function, as demonstrated by the reductions in relative kidney weight (% of body weight) and blood urea nitrogen, and the increase in the creatinine clearance capacity. GSE attenuated the As-induced changes in the serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-1β and the mRNA levels of TGF-β1, α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and fibronectin (FN) in renal tissue. Furthermore, administration of GSE markedly reduced As-stimulated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and Nox activity, as well as the protein expression levels of the NADPH subunits (Nox2, p47phox and Nox4). In addition, GSE cotreatment was correlated with a significant reduction in TGF-β/Smad signaling, as demonstrated by the decreased protein levels of TGF-β1 and pSmad2/3 in renal tissue. This study indicated that GSE may be a useful agent for the prevention of nephrotoxicity induced by chronic exposure to As. GSE may exert its effects through the suppression of Nox and inhibition of TGF-β/Smad signaling activation.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; TGF-β/Smad; chronic arsenic exposure; grape seed extract; nephrotoxicity; oxidative stress.
Figures

References
-
- Bao L, Shi H. Potential molecular mechanisms for combined toxicity of arsenic and alcohol. J Inorg Biochem. 2010;104:1229–1233. - PubMed
-
- Eom SY, Lee YC, Yim DH, Lee CH, Kim YD, Choi BS, Park CH, Yu SD, Kim DS, Park JD, Kim H. Effects of low-level arsenic exposure on urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase activity. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2011;30:1885–1891. - PubMed
-
- Chen JW, Chen HY, Li WF, Liou SH, Chen CJ, Wu JH, Wang SL. The association between total urinary arsenic concentration and renal dysfunction in a community-based population from central Taiwan. Chemosphere. 2011;84:17–24. - PubMed
-
- Kitchin KT. Recent advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001;172:249–261. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
