Chromosomal characterization of the three subgenomes in the polyploids of Hordeum murinum L.: new insight into the evolution of this complex
- PMID: 24349062
- PMCID: PMC3862567
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081385
Chromosomal characterization of the three subgenomes in the polyploids of Hordeum murinum L.: new insight into the evolution of this complex
Abstract
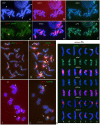
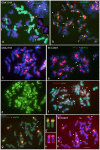
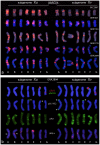
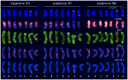
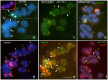
Hordeum murinum L. is a species complex composed of related taxa, including the subspecies glaucum, murinum and leporinum. However, the phylogenetic relationships between the different taxa and their cytotypes, and the origin of the polyploid forms, remain points of controversy. The present work reports a comparative karyotype analysis of seven accessions of the H. murinum complex representing all subspecies and cytotypes. The karyotypes were determined by examining the distribution of the repetitive Triticeae DNA sequences pTa71, pTa794, pSc119.2, pAs1 and pHch950, the simple sequence repeats (SSRs) (AG)10, (AAC)5, (AAG)5, (ACT)5, (ATC)5, and (CCCTAAA)3 via in situ hybridization. The chromosomes of the three subgenomes involved in the polyploids were identified. All tetraploids of all subspecies shared the same two subgenomes (thus suggesting them to in fact belong to the same taxon), the result of hybridization between two diploid ancestors. One of the subgenomes present in all tetraploids of all subspecies was found to be very similar (though not identical) to the chromosome complement of the diploid glaucum. The hexaploid form of leporinum came about through a cross between a tetraploid and a third diploid form. Exclusively bivalent associations among homologous chromosomes were observed when analyzing pollen mother cells of tetraploid taxa. In conclusion, the present results identify all the individual chromosomes within the H. murinum complex, reveal its genome structure and phylogeny, and explain the appearance of the different cytotypes. Three cryptic species are proposed according to ploidy level that may deserve full taxonomic recognition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Van de Peer Y, Maere S, Meyer A (2009) The evolutionary significance of ancient genome duplications. Nat Rev Genet 10: 725–732. - PubMed
-
- Bothmer RV, Flink J, Landström T (1986) Meiosis in interspecific Hordeum hybrids. I. Diploid combinations. Can J Genet Cytol 28: 525–535.
-
- Bothmer RV, Flink J, Landström T (1987) Meiosis in interspecific Hordeum hybrids. II. Triploid combinations. Evol. Trends Plants 1: 41–50.
-
- Linde-Laursen I, Bothmer RV, Jacobsen N (1992) Relationships in the genus Hordeum: Giemsa C-banded karyotypes. Hereditas 116: 111–116.
-
- Wang RRC, Bothmer RV, Dvorak J, Fedak G, Linde-Laursen I, et al. (1996) Genome symbols in the Triticeae In: Wang RRC, Jensen KB and Jaussi C (eds) Proceedings of the 2nd International Triticeae Symposium, Utah State University, Logan, pp 29–34
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

