Elevated plasma SPARC levels are associated with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 24349098
- PMCID: PMC3857203
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081615
Elevated plasma SPARC levels are associated with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objective: Recent studies suggested that secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC), a novel adipokine, is a key player in the pathology of obesity and type 2 diabetes. We aimed to determine whether concentrations of SPARC were altered in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) compared to normal glucose tolerance (NGT) controls and to investigate the relationships between SPARC and metabolic parameters in pregnant women.
Design/methods: Cross-sectional study of 120 pregnant women with GDM and 60 controls with NGT, in a university hospital setting. Plasma levels of SPARC, adiponectin, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), insulin and proinsulin were determined by ELISA.
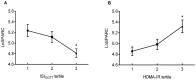
Results: GDM women had higher SPARC and lower adiponectin than NGT subjects; no difference was found in FGF21. SPARC levels were the lowest in subjects in the third tertile of insulin sensitivity index (ISIOGTT) and correlated positively with pre-pregnant BMI, insulin and 3 h glucose during 100-g OGTT, HOMA-IR, fasting proinsulin, hsCRP and white blood cells count, and negatively with ISIOGTT, when adjusting for gestational age. Triglyceride (TG), Apolipoprotein A1, apolipoprotein B and lipoprotein (a) correlated with SPARC in partial Pearson correlation. Correlations between SPARC with adiponectin, systolic blood pressure and TG were marginally significant in partial Spearman correlation analysis. In multivariate regression analysis, SPARC was an independent negative indicator of ISIOGTT.
Conclusions: SPARC levels are correlated significantly with inflammation and may also be correlated with dyslipidemia and represent an independent determinant of insulin resistance in late pregnancy, indicating a potential role of SPARC in the pathophysiology of GDM.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Associateion (2007) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 30 Suppl 1S42–47. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara A (2007) Increasing prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus: a public health perspective. Diabetes Care 30 Suppl 2S141–146. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter MW (2007) Gestational diabetes, pregnancy hypertension, and late vascular disease. Diabetes Care 30 Suppl 2S246–250. - PubMed
-
- Greenberg AS, McDaniel ML (2002) Identifying the links between obesity, insulin resistance and beta-cell function: potential role of adipocyte-derived cytokines in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Eur J Clin Invest 32 Suppl 324–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

