Diagnosis of severe fetal anemia based on perinatal outcomes: a comparative analysis of the current reference values
- PMID: 24349768
- PMCID: PMC3854004
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/351258
Diagnosis of severe fetal anemia based on perinatal outcomes: a comparative analysis of the current reference values
Abstract
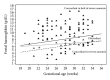
Objectives. To compare current criteria for severe fetal anemia diagnosis. Methodology. A cohort study analyzed 105 alloimmunized fetuses that underwent cordocentesis due to risk of anemia. Concordance among the diagnostic criteria for severe fetal anemia, hemoglobin deficit >7 g/dL, hemoglobin deficit ≥5 g/dL, and hemoglobin concentration <0.55 MoM, was analyzed using Cohen's Kappa index. Perinatal mortality, fetal hydrops, and fetal acidosis were used to discuss discordances. Results. There was fair concordance among the three criteria analyzed: 0.80 (Kappa index, IC 95%: 0.67 to 0.93) when comparing hemoglobin deficit >7.0 g/dL and hemoglobin concentration <0.55 MoM criteria, 0.63 (Kappa index, IC 95%: 0.47 to 0.69) when comparing hemoglobin deficit ≥5.0 g/dL and hemoglobin deficit >7.0 g/dL reference, and 0.77 (Kappa index, IC 95%: 0.64 to 0.90) when comparing hemoglobin deficit≥5.0 g/dL and hemoglobin concentration <0.55 MoM standards. Eighteen cases were classified differently depending on the criteria used. The cut-off point of hemoglobin deficit ≥5 g/dL was the best criterion to discriminate fetuses with poor perinatal outcome in our study. Conclusions. Relevant discordances in classification of severe fetal anemia were pointed out. Some criteria may underestimate the real gravity of fetal anemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined use of the cardiofemoral index and middle cerebral artery Doppler velocimetry for the prediction of fetal anemia.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2010 Dec;111(3):205-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2010.07.017. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2010. PMID: 20850744
-
A new splenic artery Doppler velocimetric index for prediction of severe fetal anemia associated with Rh alloimmunization.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Jan;180(1 Pt 1):49-54. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70148-1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 9914577
-
Middle cerebral artery Doppler velocimetric deceleration angle as a predictor of fetal anemia in Rh-alloimmunized fetuses without hydrops.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Sep;183(3):746-51. doi: 10.1067/mob.2000.106818. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000. PMID: 10992203
-
Consensus diagnostic criteria and monitoring of twin anemia-polycythemia sequence: Delphi procedure.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Sep;56(3):388-394. doi: 10.1002/uog.21882. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 31605505
-
[Review by expert group in the diagnosis and treatment of anemia in pregnant women. Federación Mexicana de Colegios de Obstetricia y Ginecología].Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2012 Sep;80(9):563-80. Ginecol Obstet Mex. 2012. PMID: 23243836 Spanish.
References
-
- Nardozza LMM, Camano L, Moron AF, et al. Perinatal mortality in Rh alloimmunized patients. European Journal of Obstetrics Gynecology and Reproductive Biology. 2007;132(2):159–162. - PubMed
-
- Nardozza LMM, Junior EA, Simioni C, Camano L, Moron AF. Intervalos de referência do pico de velocidade sistólica da artéria cerebral média fetal na população brasileira. Radiologia Brasileira. 2008;41(6):385–389.
-
- Cabral ACV, Barcelos TBD, Apocalipse IGM, Leite HV, Reis ZSN. Indice Cárdio-Femoral Para Avaliação Da Anemia De Fetos De Gestantes Isoimuniza Das. 2005.
-
- Bowman J. The management of hemolytic disease in the fetus and newborn. Seminars in Perinatology. 1997;21(1):39–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

