Clinical functional anatomy of the pterygopalatine ganglion, cephalgia and related dysautonomias: A review
- PMID: 24349865
- PMCID: PMC3858801
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.121628
Clinical functional anatomy of the pterygopalatine ganglion, cephalgia and related dysautonomias: A review
Abstract
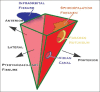
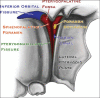
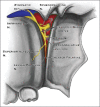
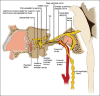
The purpose of this article is to explain the anatomy of the pterygopalatine ganglion (PPG), its location in the pterygopalatine fossa (PPF) in the skull, and the relationship it has to the Vidian nerve terminal branches and the fifth cranial nerve. An overview of the neuro-anatomical/clinical correlations, a spectrum of pathologies affecting the seventh cranial nerve and some therapies both medical and surgical are noted. The focus is the pterygopalatine region with discussion of the proximal courses of the seventh and fifth cranial nerves and their pathological processes. The ganglion is used as an example of neuro-anatomical model for explaining cluster headaches (CH). Radiological correlation is included to clarify the location of the PPF and its clinical importance.
Keywords: Cluster headaches; facial paresis; greater superficial petrosal nerve; pterygopalatine fossa; pterygopalatine ganglion; radiosurgery; seventh cranial nerve; treatment of cluster headaches.
Figures
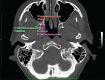
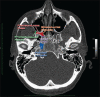
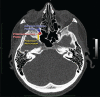
References
-
- Ahamed SH, Jones NS. What is Sluder's Neuralgia. J Laryngol Otol. 2003;117:437–43. - PubMed
-
- Alajouanine T, Thurel R. Les sympathpatalgies facials. J Med Fr. 1933;22:188–94.
-
- Alvernia JE, Spomar DG, Olivero WC. A computed tomography scan and anatomical cadaveric study of the pterygopalatine ganglion for use in Gamma Knife treatment of cluster headache. J Neurosurg. 2007;107:805–8. - PubMed
-
- Brown LA. Mythical sphenopalatine ganglion neuralgia. South Med J. 1962;55:670–2. - PubMed
-
- Chen CC, Chen XX, Yang XD, Zheng JW, Li ZP, Huang F, et al. Comparative research of the thin transverse sectional anatomy and the multislice spiral CT on pterygopalatine fossa. Turk Neurosurg. 2010;20:151–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

