Vismodegib: A smoothened inhibitor for the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24350028
- PMCID: PMC3853913
- DOI: 10.4103/2229-5178.120685
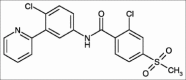
Vismodegib: A smoothened inhibitor for the treatment of advanced basal cell carcinoma
Abstract
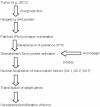
Incidence of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), the most common skin cancer in humans, is rising. Surgery is the mainstay of treatment but there is no standard of care for locally advanced or metastatic disease. Hedgehog signaling proteins are critical for cell growth and differentiation during embryogenesis; Hh pathway is silenced in adults. Dysregulated or aberrant Hh signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of BCC. This hyperactive pathway can be inhibited by use of smoothened inhibitors such as vismodegib. Food and drug administration approved this oral, once-daily medication in 2012 to treat adults with metastatic BCC or locally advanced, recurrent BCC after surgery and also for patients with locally advanced BCC who are not candidates for surgery or radiation treatment. Clinical studies have shown it to be highly efficacious and the most common adverse effects include, muscle spasms, alopecia and dysgeusia. Use of targeted biologic modifiers, exemplified by Hh directed therapeutics offer a new hope to patients with high-surgical morbidity or inoperable tumors.
Keywords: Basal cell carcinoma; hedgehog signaling pathways; vismodegib.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Malhotra P, Singh A, Ramesh V. Basal cell carcinoma in the North Indian population: Clinicopathologic review and immunohistochemical analysis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2011;77:328–30. - PubMed
-
- O’Bryan KW, Ratner D. The role of targeted molecular inhibitors in the management of advanced nonmelanoma skin cancer. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2011;30:57–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources