Acid lipase from Candida viswanathii: production, biochemical properties, and potential application
- PMID: 24350270
- PMCID: PMC3847968
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/435818
Acid lipase from Candida viswanathii: production, biochemical properties, and potential application
Abstract
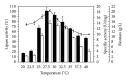
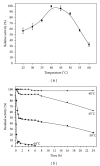
Influences of environmental variables and emulsifiers on lipase production of a Candida viswanathii strain were investigated. The highest lipase activity (101.1 U) was observed at 210 rpm, pH 6.0, and 27.5°C. Other fermentation parameters analyzed showed considerable rates of biomass yield (Y L/S = 1.381 g/g), lipase yield (Y L/S = 6.892 U/g), and biomass productivity (P X = 0.282 g/h). Addition of soybean lecithin increased lipase production in 1.45-fold, presenting lipase yield (Y L/S ) of 10.061 U/g. Crude lipase presented optimal activity at acid pH of 3.5, suggesting a new lipolytic enzyme for this genus and yeast in general. In addition, crude lipase presented high stability in acid conditions and temperature between 40 and 45°C, after 24 h of incubation in these temperatures. Lipase remained active in the presence of organic solvents maintaining above 80% activity in DMSO, methanol, acetonitrile, ethanol, acetone, 1-propanol, isopropanol, and 2-propanol. Effectiveness for the hydrolysis of a wide range of natural triglycerides suggests that this new acid lipase has high potential application in the oleochemical and food industries for hydrolysis and/or modification of triacylglycerols to improve the nutritional properties.
Figures



References
-
- Houde A, Kademi A, Leblanc D. Lipases and their industrial applications: an overview. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology Part A. 2004;118(1–3):155–170. - PubMed
-
- Feltes MMC, de Oliveira D, Block JM, Ninow JL. The production, benefits, and applications of monoacylglycerols and diacylglycerols of nutritional interest. Food and Bioprocess Technology. 2013;6:17–35.
-
- Rigo E, Ninow JL, Tsai SM, et al. Preliminary characterization of novel extra-cellular lipase from Penicillium crustosum under solid-state fermentation and its potential application for triglycerides hydrolysis. Food and Bioprocess Technology. 2012;5:1592–1600.
-
- Fernandez-Lafuente R. Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus: uses and prospects as an industrial biocatalyst. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B. 2010;62(3-4):197–212.
-
- Li N, Zong M-H. Lipases from the genus Penicillium: production, purification, characterization and applications. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B. 2010;66(1-2):43–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

