Algorithms for a closed-loop artificial pancreas: the case for proportional-integral-derivative control
- PMID: 24351189
- PMCID: PMC3876341
- DOI: 10.1177/193229681300700623
Algorithms for a closed-loop artificial pancreas: the case for proportional-integral-derivative control
Abstract
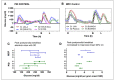
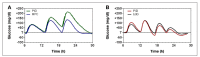
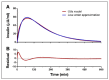
Closed-loop insulin delivery continues to be one of most promising strategies for achieving near-normal control of blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes. Of the many components that need to work well for the artificial pancreas to be advanced into routine use, the algorithm used to calculate insulin delivery has received a substantial amount of attention. Most of that attention has focused on the relative merits of proportional-integral-derivative versus model-predictive control. A meta-analysis of the clinical data obtained in studies performed to date with these approaches is conducted here, with the objective of determining if there is a trend for one approach to be performing better than the other approach. Challenges associated with implementing each approach are reviewed with the objective of determining how these approaches might be improved. Results of the meta-analysis, which focused predominantly on the breakfast meal response, suggest that to date, the two approaches have performed similarly. However, uncontrolled variables among the various studies, and the possibility that future improvements could still be effected in either approach, limit the validity of this conclusion. It is suggested that a more detailed examination of the challenges associated with implementing each approach be conducted.
© 2013 Diabetes Technology Society.
Figures


Comment in
-
Algorithms for a closed-loop artificial pancreas: the case for model predictive control.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013 Nov 1;7(6):1632-43. doi: 10.1177/193229681300700624. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2013. PMID: 24351190 Free PMC article.
-
Ongoing Debate About Models for Artificial Pancreas Systems and In Silico Studies.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018 Mar;20(3):174-176. doi: 10.1089/dia.2018.0038. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29565720 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Steil GM, Rebrin K, Darwin C, Hariri F, Saad MF. Feasibility of automating insulin delivery for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006;55(12):3344–3350. - PubMed
-
- Weinzimer SA, Steil GM, Swan KL, Dziura J, Kurtz N, Tamborlane WV. Fully automated closed-loop insulin delivery versus semiautomated hybrid control in pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes using an artificial pancreas. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(5):934–939. - PubMed
-
- Wolpert HA, Atakov-Castillo A, Smith SA, Steil GM. Dietary fat acutely increases glucose concentrations and insulin requirements in patients with type 1 diabetes: implications for carbohydrate-based bolus dose calculation and intensive diabetes management. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(4):810–816. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

