The effect of conformational variability of phosphotriesterase upon N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone and paraoxon binding: insights from molecular dynamics studies
- PMID: 24352010
- PMCID: PMC6269825
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules181215501
The effect of conformational variability of phosphotriesterase upon N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone and paraoxon binding: insights from molecular dynamics studies
Abstract
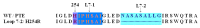
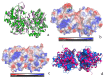
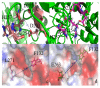
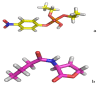
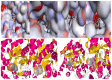
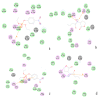
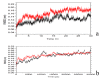
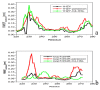
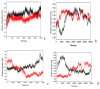
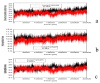
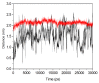
The organophosphorous hydrolase (PTE) from Brevundimonas diminuta is capable of degrading extremely toxic organophosphorous compounds with a high catalytic turnover and broad substrate specificity. Although the natural substrate for PTE is unknown, its loop remodeling (loop 7-2/H254R) led to the emergence of a homoserine lactonase (HSL) activity that is undetectable in PTE (kcat/km values of up to 2 × 10(4)), with only a minor decrease in PTE paraoxonase activity. In this study, homology modeling and molecular dynamics simulations have been undertaken seeking to explain the reason for the substrate specificity for the wild-type and the loop 7-2/H254R variant. The cavity volume estimated results showed that the active pocket of the variant was almost two fold larger than that of the wild-type (WT) enzyme. pKa calculations for the enzyme (the WT and the variant) showed a significant pKa shift from WT standard values (ΔpKa = 3.5 units) for the His254 residue (in the Arg254 variant). Molecular dynamics simulations indicated that the displacement of loops 6 and 7 over the active site in loop 7-2/H254R variant is useful for N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL) with a large aliphatic chain to site in the channels easily. Thence the expanding of the active pocket is beneficial to C4-HSL binding and has a little effect on paraoxon binding. Our results provide a new theoretical contribution of loop remodeling to the rapid divergence of new enzyme functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stereoselectivity of phosphotriesterase with paraoxon derivatives: a computational study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016;34(3):600-11. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2015.1046937. Epub 2015 Jun 15. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016. PMID: 25929154
-
Binding modes of phosphotriesterase-like lactonase complexed with δ-nonanoic lactone and paraoxon using molecular dynamics simulations.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017 Feb;35(2):273-286. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2016.1142899. Epub 2016 Mar 4. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017. PMID: 26775655
-
Functional annotation and three-dimensional structure of Dr0930 from Deinococcus radiodurans, a close relative of phosphotriesterase in the amidohydrolase superfamily.Biochemistry. 2009 Mar 17;48(10):2237-47. doi: 10.1021/bi802274f. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19159332 Free PMC article.
-
Detoxification of organophosphate nerve agents by bacterial phosphotriesterase.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005 Sep 1;207(2 Suppl):459-70. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.02.025. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15982683 Review.
-
Lactonases with organophosphatase activity: structural and evolutionary perspectives.Chem Biol Interact. 2010 Sep 6;187(1-3):370-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.039. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Chem Biol Interact. 2010. PMID: 20122908 Review.
Cited by
-
Theoretical study on the allosteric regulation of an oligomeric protease from Pyrococcus horikoshii by Cl- Ion.Molecules. 2014 Feb 7;19(2):1828-42. doi: 10.3390/molecules19021828. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24514746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benschop H.P., de Jong L.P.A. Nerve agent stereoisomers: Analysis, isolation, and toxicology. Acc. Chem. Res. 1988;21:368–374. doi: 10.1021/ar00154a003. - DOI
-
- Ordentlich A., Barak D., Sod-Moriah G., Kaplan D., Mizrahi D., Segall Y., Kronman C., Karton Y., Lazar A., Marcus D., et al. Stereoselectivity toward VX is determined by interactions with residues of the acyl pocket as well as of the peripheral anionic site of AChE. Biochemistry. 2004;43:11255–11265. doi: 10.1021/bi0490946. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

