Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA binding protein DRB3 participates in methylation-mediated defense against geminiviruses
- PMID: 24352449
- PMCID: PMC3958096
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02305-13
Arabidopsis double-stranded RNA binding protein DRB3 participates in methylation-mediated defense against geminiviruses
Abstract
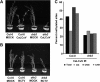
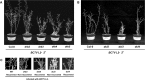
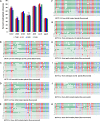
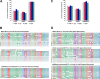
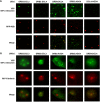
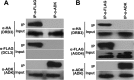
Arabidopsis encodes five double-stranded RNA binding (DRB) proteins. DRB1 and DRB2 are involved in microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis, while DRB4 functions in cytoplasmic posttranscriptional small interfering RNA (siRNA) pathways. DRB3 and DRB5 are not involved in double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) processing but assist in silencing transcripts targeted by DRB2-associated miRNAs. The goal of this study was to determine which, if any, of the DRB proteins might also participate in a nuclear siRNA pathway that leads to geminivirus genome methylation. Here, we demonstrate that DRB3 functions with Dicer-like 3 (DCL3) and Argonaute 4 (AGO4) in methylation-mediated antiviral defense. Plants employ repressive viral genome methylation as an epigenetic defense against geminiviruses, using an RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) pathway similar to that used to suppress endogenous invasive DNAs such as transposons. Chromatin methylation inhibits virus replication and transcription, and methylation-deficient host plants are hypersusceptible to geminivirus infection. Using a panel of drb mutants, we found that drb3 plants uniquely exhibit a similar hypersensitivity and that viral genome methylation is substantially reduced in drb3 compared to wild-type plants. In addition, like dcl3 and ago4 mutants, drb3 plants fail to recover from infection and cannot accomplish the viral genome hypermethylation that is invariably observed in asymptomatic, recovered tissues. Small RNA analysis, bimolecular fluorescence complementation, and coimmunoprecipitation experiments show that DRB3 acts downstream of siRNA biogenesis and suggest that it associates with DCL3 and AGO4 in distinct subnuclear compartments. These studies reveal that in addition to its previously established role in the miRNA pathway, DRB3 also functions in antiviral RdDM.
Importance: Plants use RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) as an epigenetic defense against geminiviruses. RNA silencing pathways in Arabidopsis include five double-stranded RNA binding proteins (DRBs) related to Drosophila R2D2 and mammalian TRBP and PACT. While DRB proteins have defined roles in miRNA and cytoplasmic siRNA pathways, a role in nuclear RdDM was elusive. Here, we used the geminivirus system to show that DRB3 is involved in methylation-mediated antiviral defense. Beginning with a panel of Arabidopsis drb mutants, we demonstrated that drb3 plants uniquely show enhanced susceptibility to geminiviruses. Further, like dcl3 and ago4 mutants, drb3 plants fail to hypermethylate the viral genome, a requirement for host recovery. We also show that DRB3 physically interacts with the RdDM pathway components DCL3 and AGO4 in the nucleus. This work highlights the utility of geminiviruses as models for de novo RdDM and places DRB3 protein in this fundamental epigenetic pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DRB2, DRB3 and DRB5 function in a non-canonical microRNA pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Oct 1;7(10):1224-9. doi: 10.4161/psb.21518. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22902697 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of plant dsRNA-binding proteins in RNAi-like pathways.FEBS Lett. 2008 Aug 6;582(18):2753-60. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.07.004. Epub 2008 Jul 14. FEBS Lett. 2008. PMID: 18625233
-
Double-stranded RNA-binding protein DRB3 negatively regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis by modulating PAP1 expression in Arabidopsis thaliana.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):45-55. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0886-0. Epub 2016 Dec 19. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27995376
-
Plant dicer-like proteins: double-stranded RNA-cleaving enzymes for small RNA biogenesis.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):33-44. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0877-1. Epub 2016 Nov 24. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27885504 Review.
-
Dissecting the roles of TRBP and PACT in double-stranded RNA recognition and processing of noncoding RNAs.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015 May-Jun;6(3):271-89. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1272. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015. PMID: 25630541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Glimpse of "Dicer Biology" Through the Structural and Functional Perspective.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 7;8:643657. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.643657. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Characterization of Replication-Associated Proteins Encoded by Alphasatellites Identified in Yunnan Province, China.Viruses. 2022 Jan 24;14(2):222. doi: 10.3390/v14020222. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35215816 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated single-base resolution maps of transcriptome, sRNAome and methylome of Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) in tomato.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 27;9(1):2863. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39239-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30814535 Free PMC article.
-
The Search for Resistance to Cassava Mosaic Geminiviruses: How Much We Have Accomplished, and What Lies Ahead.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Mar 24;8:408. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00408. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28392798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNAi-Based Antiviral Innate Immunity in Plants.Viruses. 2022 Feb 20;14(2):432. doi: 10.3390/v14020432. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35216025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

