DSPP contains an IRES element responsible for the translation of dentin phosphophoryn
- PMID: 24352500
- PMCID: PMC3895336
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034513516631
DSPP contains an IRES element responsible for the translation of dentin phosphophoryn
Abstract
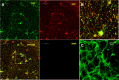
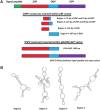
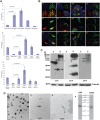
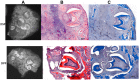
The major phosphoprotein in dentin is the aspartic acid and serine-rich protein called dentin phosphophoryn (DPP). DPP appears to be synthesized as a part of a larger compound protein, dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP). DSPP has never been isolated or detected in dentin extracts. It is now evident that DSPP is a chimeric protein composed of 3 parts: dentin sialoprotein (DSP), DPP, and dentin glycoprotein (DGP). Previous reports have suggested that the BMP1 protease is responsible for processing DSPP. However, unequal amounts of these products are present in the dentin matrix. Here, we provide evidence for an internal ribosome entry site in the DSPP gene that directs the synthesis of DPP. This mechanism would account for unequal amounts of intracellular DSP and DPP. The internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) activity varied in different cell types, suggesting the presence of additional regulatory elements during the translational regulation of DPP. Further, we provide evidence that DPP is transported to the extracellular matrix (ECM) through exosomes. Using tissue recombination and lentivirus-mediated gain-of-function approaches, we also demonstrate that DPP is essential for the formation of well-defined tooth structures with mineralized dentin matrix.
Keywords: cell biology; cell differentiation; dentin; extracellular matrix (ECM); matrix biology; odontoblast(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publications of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Alvares K, Kanwar YS, Veis A. (2006). Expression and potential role of dentin phosphophoryn (DPP) in mouse embryonic tissues involved in epithelial-mesenchymal interactions and branching morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 235:2980-2990. - PubMed
-
- Bailleul-Forestier I, Molla M, Verloes A, Berdal A. (2008). The genetic basis of inherited anomalies of the teeth. Part 1: Clinical and molecular aspects of non-syndromic dental disorders. Eur J Med Genet 51:273-291. - PubMed
-
- Bègue-Kirn C, Krebsbach PH, Bartlett JD, Butler WT. (1998). Dentin sialoprotein, dentin phosphoprotein, enamelysin and ameloblastin: tooth-specific molecules that are distinctly expressed during murine dental differentiation. Eur J Oral Sci 106:963-970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

