Constructing and characterizing a bioactive small molecule and microRNA association network for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 24352679
- PMCID: PMC3899875
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2013.1057
Constructing and characterizing a bioactive small molecule and microRNA association network for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
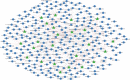
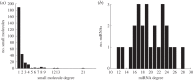
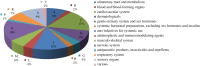
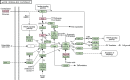
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is an incurable neurodegenerative disorder. Much effort has been devoted to developing effective therapeutic agents. Recently, targeting microRNAs (miRNAs) with small molecules has become a novel therapy for human diseases. In this study, we present a systematic computational approach to construct a bioactive Small molecule and miRNA association Network in AD (SmiRN-AD), which is based on the gene expression signatures of bioactive small molecule perturbation and AD-related miRNA regulation. We also performed topological and functional analysis of the SmiRN-AD from multiple perspectives. At the significance level of p ≤ 0.01, 496 small molecule-miRNA associations, including 25 AD-related miRNAs and 275 small molecules, were recognized and used to construct the SmiRN-AD. The drugs that were connected with the same miRNA tended to share common drug targets (p = 1.72 × 10(-4)) and belong to the same therapeutic category (p = 4.22 × 10(-8)). The miRNAs that were linked to the same small molecule regulated more common miRNA targets (p = 6.07 × 10(-3)). Further analysis of the positive connections (quinostatin and miR-148b, amantadine and miR-15a) and the negative connections (melatonin and miR-30e-5p) indicated that our large-scale predictions afforded specific biological insights into AD pathogenesis and therapy. This study proposes a holistic strategy for deciphering the associations between small molecules and miRNAs in AD, which may be helpful for developing a novel effective miRNA-associated therapeutic strategy for AD. A comprehensive database for the SmiRN-AD and the differential expression patterns of the miRNA targets in AD is freely available at http://bioinfo.hrbmu.edu.cn/SmiRN-AD/.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; bioinformatics; drug; microRNA; small molecule; therapeutics.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
