Clinical application of the Provox NiD voice prosthesis: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 24352975
- PMCID: PMC4048322
- DOI: 10.1002/lary.24488
Clinical application of the Provox NiD voice prosthesis: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Objectives/hypothesis: To evaluate the indications, complications, and device life of the Provox NiD in a large cohort at a tertiary US cancer center.
Study design: Longitudinal retrospective cohort study.
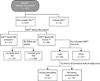
Methods: We reviewed the records of patients who used the NiD prosthesis (2005-2011) for general indicators, device life, and complications.
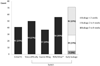
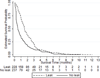
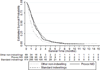
Results: One hundred eighty-six patients who used the NiD were included (median follow-up: 21.4 months). The NiD was placed at initial fit in 41 (22%) patients, whereas 145 (78%) tried an NiD after using another type of prosthesis. Most patients used the NiD similarly to an indwelling device. Median NiD device life was significantly longer than that of other nonindwelling prostheses (45 vs. 29 days, P=.0061), and did not significantly differ from that of standard indwelling devices (45 vs. 50 days, P=.4263). Thirty-eight percent (71 of 189) of NiD users had a history of early leakage (<8 weeks) using a different prosthesis before trying the NiD. Among patients with a pre-existing history of early leakage, almost 90% of NiD prostheses outperformed the device life of other products.
Conclusions: The NiD prosthesis offers satisfactory device life on a par with indwelling prostheses in our cohort of NiD users. Coupled with favorable published airflow characteristics and satisfactory tracheoesophageal voice, these data suggest that the NiD offers a durable, low-cost prosthetic alternative in contemporary practice. A unique indication for NiD may be improved device life in some patients with a history of early leakage.
Level of evidence: 4.
Keywords: Provox NiD; total laryngectomy; tracheoesophageal puncture; voice prosthesis.
© 2013 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None
Figures



References
-
- Lewin JS, Hutcheson KA. General Principles of rehabilitation of speech, voice, and swallowing function after treatment of head and neck cancer. In: Harrison LB, Sessions RB, Hong WK, editors. Head and Neck Cancer A Multidisciplinary Approach. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009. pp. 168–177.
-
- Vlantis AC, Gregor RT, Elliot H, Oudes M. Conversion from a non-indwelling to a Provox2 indwelling voice prosthesis for speech rehabilitation: comparison of voice quality and patient preference. J Laryngol Otol. 2003;117(10):815–820. - PubMed
-
- Hancock K, Houghton B, Van As-Brooks CJ, Coman W. First clinical experience with a new non-indwelling voice prosthesis (Provox® NID™) for voice rehabilitation after total laryngectomy. Acta Otolaryngol. 2005;125(9):981–990. - PubMed
-
- Leder SB, Sasaki CT. Incidence, timing, and importance of tracheoesophageal prosthesis resizing for successful tracheoesophageal speech production. Laryngoscope. 1995;105(8 Pt. 1):827–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

