Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors enhance chemotherapy killing in gastrointestinal/genitourinary cancer cells
- PMID: 24353313
- PMCID: PMC3935155
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.113.090043
Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors enhance chemotherapy killing in gastrointestinal/genitourinary cancer cells
Abstract
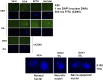
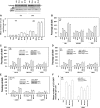
The present studies determined whether clinically relevant phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors interacted with clinically relevant chemotherapies to kill gastrointestinal/genitourinary cancer cells. In bladder cancer cells, regardless of H-RAS mutational status, at clinically achievable doses, PDE5 inhibitors interacted in a greater than additive fashion with doxorubicin/mitomycin C/gemcitabine/cisplatin/paclitaxel to cause cell death. In pancreatic tumor cells expressing mutant active K-RAS, PDE5 inhibitors interacted in a greater than additive fashion with doxorubicin/gemcitabine/paclitaxel to cause cell death. The most potent PDE5 inhibitor was sildenafil. Knock down of PDE5 expression recapitulated the combination effects of PDE5 inhibitor drugs with chemotherapy drugs. Expression of cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein-short did not significantly inhibit chemotherapy lethality but did significantly reduce enhanced killing in combination with sildenafil. Overexpression of B-cell lymphoma-extra large suppressed individual and combination drug toxicities. Knock down of CD95 or Fas-associated death domain protein suppressed drug combination toxicity. Combination toxicity was also abolished by necrostatin or receptor interacting protein 1 knock down. Treatment with PDE5 inhibitors and chemotherapy drugs promoted autophagy, which was maximal at ∼24 hour posttreatment, and 3-methyl adenine or knock down of Beclin1 suppressed drug combination lethality by ∼50%. PDE5 inhibitors enhanced and prolonged the induction of DNA damage as judged by Comet assays and γhistone 2AX (γH2AX) and checkpoint kinase 2 (CHK2) phosphorylation. Knock down of ataxia telangiectasia mutated suppressed γH2AX and CHK2 phosphorylation and enhanced drug combination lethality. Collectively our data demonstrate that the combination of PDE5 inhibitors with standard of care chemotherapy agents for gastrointestinal/genitourinary cancers represents a novel modality.
Figures






References
-
- Antoni L, Sodha N, Collins I, Garrett MD. (2007) CHK2 kinase: cancer susceptibility and cancer therapy - two sides of the same coin? Nat Rev Cancer 7:925–936 - PubMed
-
- Bender AT, Beavo JA. (2006) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev 58:488–520 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

