The de ritis ratio: the test of time
- PMID: 24353357
- PMCID: PMC3866949
The de ritis ratio: the test of time
Abstract
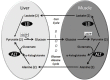
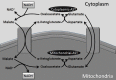
De Ritis described the ratio between the serum levels of aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) almost 50 years ago. While initially described as a characteristic of acute viral hepatitis where ALT was usually higher than AST, other authors have subsequently found it useful in alcoholic hepatitis, where AST is usually higher than ALT. These interpretations are far too simplistic however as acute viral hepatitis can have AST greater than ALT, and this can be a sign of fulminant disease, while alcoholic hepatitis can have ALT greater than AST when several days have elapsed since alcohol exposure. The ratio therefore represents the time course and aggressiveness of disease that would be predicted from the relatively short half-life of AST (18 h) compared to ALT (36 h). In chronic viral illnesses such as chronic viral hepatitis and chronic alcoholism as well as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, an elevated AST/ALT ratio is predictive of long terms complications including fibrosis and cirrhosis. There are methodological issues, particularly whether or not pyridoxal phosphate is used in the transaminase assays, and although this can have specific effects when patient samples are deficient in this vitamin, these method differences generally have mild effects on the usefulness of the assays or the ratio. Ideally laboratories should be using pyridoxal phosphate supplemented assays in alcoholic, elderly and cancer patients who may be pyridoxine deplete. Ideally all laboratories reporting abnormal ALT should also report AST and calculate the De Ritis ratio because it provides useful diagnostic and prognostic information.
Figures
References
-
- De Ritis F, Coltorti M, Giusti G. An enzymic test for the diagnosis of viral hepatitis; the transaminase serum activities. Clin Chim Acta. 1957;2:70–4. - PubMed
-
- Rej R. Aspartate aminotransferase activity and isoenzyme proportions in human liver tissues. Clin Chem. 1978;24:1971–9. - PubMed
-
- King J. Practical Clinical Enzymology. London: D Van Nostrand Company Limited; 1965.
-
- Kamimoto Y, Horiuchi S, Tanase S, Morino Y. Plasma clearance of intravenously injected aspartate aminotransferase isozymes: evidence for preferential uptake by sinusoidal liver cells. Hepatology. 1985;5:367–75. - PubMed
-
- Feldstein AE, Canbay A, Angulo P, Taniai M, Burgart LJ, Lindor KD, et al. Hepatocyte apoptosis and fas expression are prominent features of human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:437–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources