Irreversible Horner's syndrome diagnosed by aproclonidine test due to benign thyroid nodule
- PMID: 24353546
- PMCID: PMC3809183
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.291.2732
Irreversible Horner's syndrome diagnosed by aproclonidine test due to benign thyroid nodule
Abstract
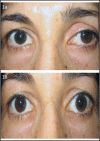
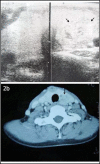
We are reporting an irreversible Horner Syndrome (HS) in a patient with benign thyroid gland nodule in which thyroidectomy was performed for treatment. A 37-year-old female was admitted to our clinic with a swelling in the left lobe of the thyroid gland and ptosis at the left eyelid. The clinical diagnosis of HS was confirmed pharmacologically by aproclonidine. Histopathologic examination of thyroidectomy specimen was reported as benign nodule. To the best of our knowledge, this is a very rare report in terms of thyroid benign nodule associated with irreversible HS due to cervical sympathetic chain compression.
Keywords: Aproclonidine; Horner’s syndrome; Thyroid nodule.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Benign thyroid swelling presenting as Horner's syndrome.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Dec 12;13(12):e235313. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-235313. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33310822 Free PMC article.
-
Horner's Syndrome and Lymphocele Following Thyroid Surgery.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 6;12(2):474. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020474. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Horner's syndrome after an ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration puncture of a thyroid nodule.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2025 Apr 7;2025(2):e250016. doi: 10.1530/EDM-25-0016. Print 2025 Apr 1. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40192711 Free PMC article.
-
Horner's syndrome: an unusual complication of thyroidectomy: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2016 Oct 26;10(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-1072-7. J Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27784321 Free PMC article.
-
Horner's syndrome and thyroid neoplasms.ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2002 Jan-Feb;64(1):49-52. doi: 10.1159/000049270. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2002. PMID: 11891400 Review.
Cited by
-
Benign thyroid swelling presenting as Horner's syndrome.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Dec 12;13(12):e235313. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-235313. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33310822 Free PMC article.
-
Horner's Syndrome and Lymphocele Following Thyroid Surgery.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 6;12(2):474. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020474. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Walton KA, Buono LM. Horner’s syndrome. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2003;14(6):357–363. - PubMed
-
- Niedziela M. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules in children. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006;13(2):427–453. - PubMed
-
- Bayram F, Kulahli I, Yuce I, Gokce C, Cagli S, Deniz K. Functional lingual thyroid as unusual cause of progressive Dysphagia. Thyroid. 2004;14(4):321–324. - PubMed
-
- Gokce C, Patiroğlu T, Aksehirli S, Durak AC, Kelestimur F. Hydatic cyst in the thyroid gland diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Thyroid. 2003;13(10):987–989. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
