A meta-analysis on the EBV DNA and VCA-IgA in diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- PMID: 24353651
- PMCID: PMC3809314
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.293.2907
A meta-analysis on the EBV DNA and VCA-IgA in diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: We conducted a meta-analysis to compare the EBV DNA and VCA-IgA in diagnosis of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, and provide important evidence for screening method of NPC.
Methodology: Three databases, Medline (from Jan. 1966 to Jan. 2012), EMBASE (from January 1988 to Jan. 2012) and Chinese Biomedical Database (from January 1980 to Jan. 2012) were used to detect the role of EBV DNA and VCA-IgA in diagnosis of NPC. Meta-DiSc statistical software was used for analysis.
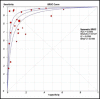
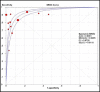
Results: Twenty seven case-control and cohort studies were included in final analysis. A total of 1554 cases and 2932 controls were included in our meta-analysis. The Sensitivity specificity, positive likelihood (+LR) and likelihood negative (-LR) of EBV-DNA in diagnosis of NPC were 0.75(0.72-0.76), 0.87(0.85-0.88), 6.98(4.50-10.83) and 0.18(0.11-0.29), respectively, and they were 0.83(0.81-0.85), 0.85(0.83-0.86), 10.89(5.41-21.93) and 0.20(0.14-0.29) for VCA-IgA. The SROC for EBV DNA detection was 0.939, while this was 0.936 for VCA-IgA detection. The subgroup analysis showed EBV-DNA had larger areas under the summary receiver operator curve when compared with VCA-IgA in high quality and low quality studies.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis indicated the EBV DNA had higher sensitivity and specificity in diagnosis of NPC.
Keywords: DNA; Diagnosis; Epstein-Barr virus (EBV); Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma; VCA-IgA.
Figures
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74–08. - PubMed
-
- Henle G, Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976;17:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Y, Zhang LG, Wu YC, Huang YS, Huang NQ, Li JY, et al. Prospective studies on nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Epstein-Barr virus IgA/VCA antibody-positive persons in Wuzhou city, China. Int J Cancer. 1985;36(5):545–547. - PubMed
-
- Cheng WM, Chan KH, Chen HL, Luo RX, Ng SP, Luk W, et al. Assessing the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma on the basis of EBV antibody spectrum. Int J Cancer. 2002;97(4):489–492. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous