Learning curve of septoplasty with radiofrequency volume reduction of the inferior turbinate
- PMID: 24353863
- PMCID: PMC3863672
- DOI: 10.3342/ceo.2013.6.4.231
Learning curve of septoplasty with radiofrequency volume reduction of the inferior turbinate
Abstract
Objectives: Since few studies on surgical training and learning curves have been performed, majority of inexperienced surgeons are anxious about performing operations. We aimed to access the results and learning curve of septoplasty with radiofrequency volume reduction (RFVR) of the inferior turbinate.
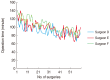
Methods: We included 270 patients who underwent septoplasty with RFVR of the inferior turbinate by 6 inexperienced surgeons between January 2009 and July 2011. We analyzed success score, cases of revision, cases of complication, operation time, and acoustic rhinometry.
Results: Success score was relatively high and every surgeon had few cases of revision and complication. No significant difference was found in success score, revision, complication case, or acoustic rhinometry values between early cases and later cases. Operation time decreased according to increase in experience. However, there was no significant difference in the operation time after more than 30 cases.
Conclusion: We can conclude that 30 cases are needed to develop mature surgical skills for septoplasty with RFVR of the inferior turbinate and that training surgeons do not need to be anxious about performing this operation in the unskilled state.
Keywords: Nasal Concha; Nasal septum; Operative procedure; Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized clinical study: outcome of submucous resection of compensatory inferior turbinate during septoplasty.Rhinology. 2011 Mar;49(1):53-7. doi: 10.4193/Rhino10.006. Rhinology. 2011. PMID: 21468375 Clinical Trial.
-
Complication Rates Following Septoplasty With Inferior Turbinate Reduction.Ochsner J. 2019 Winter;19(4):353-356. doi: 10.31486/toj.19.0002. Ochsner J. 2019. PMID: 31903059 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement in minimal cross-sectional area and nasal-cavity volume occurs in different areas after septoplasty and radiofrequency therapy of inferior turbinates.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018 Aug;275(8):1995-2003. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5022-4. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 29869709
-
Clinical Consensus Statement: Septoplasty with or without Inferior Turbinate Reduction.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Nov;153(5):708-20. doi: 10.1177/0194599815606435. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015. PMID: 26527752 Review.
-
[Surgical techniques of the inferior nasal turbinates in the treatment of nasal obstruction].Duodecim. 2010;126(17):2023-31. Duodecim. 2010. PMID: 21053519 Review. Finnish.
Cited by
-
Cumulative Sum Analysis of the Learning Curve of Free Flap Reconstruction in Head and Neck Cancer Patients.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 May;15(2):177-182. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2021.01053. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35249319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babineau TJ, Becker J, Gibbons G, Sentovich S, Hess D, Robertson S, et al. The "cost" of operative training for surgical residents. Arch Surg. 2004 Apr;139(4):366–369. - PubMed
-
- Bridges M, Diamond DL. The financial impact of teaching surgical residents in the operating room. Am J Surg. 1999 Jan;177(1):28–32. - PubMed
-
- Koperna T. How long do we need teaching in the operating room? The true costs of achieving surgical routine. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2004 Jun;389(3):204–208. - PubMed
-
- Wang MC, Yu EC, Shiao AS, Liao WH, Liu CY. The costs and quality of operative training for residents in tympanoplasty type I. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009 May;129(5):512–514. - PubMed
-
- Bokhari AR, Davies MA, Diamond T. Endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: a single surgeon experience and the learning curve. Br J Neurosurg. 2013 Feb;27(1):44–49. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources