New prospects on the NKG2D/NKG2DL system for oncology
- PMID: 24353908
- PMCID: PMC3862635
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.26097
New prospects on the NKG2D/NKG2DL system for oncology
Abstract
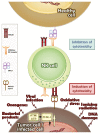
The activating immunoreceptor NKG2D endows cytotoxic lymphocytes with the capacity to recognize and eliminate infected or malignant cells. The recognition of such harmful cells is enabled by binding of NKG2D to various MHC class I-related glycoproteins, which are upregulated in the course of viral infection or malignant transformation. The past years have witnessed substantial progress in our understanding of the mechanisms underlying the regulation of NKG2D ligands (NKG2DLs) by malignant cells, of tumor-associated countermeasures promoting escape from NKG2D-dependent immunosurveillance, and of therapeutic measures that may bolster the NKG2D/NKG2DL system against malignancies. Here, we summarize the current knowledge on the NKG2D/NKG2DL system and outline opportunities to exploit the tumoricidal function of NKG2D for anticancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: MIC; NK cell; NKG2D; Rae; T cell; ULBP; immune escape; tumor immunology.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
