Transcranial magnetic stimulation in neurology: A review of established and prospective applications
- PMID: 24353923
- PMCID: PMC3863979
- DOI: 10.1212/01.CPJ.0000436213.11132.8e
Transcranial magnetic stimulation in neurology: A review of established and prospective applications
Abstract
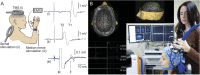
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a neurophysiologic technique to noninvasively induce a controlled current pulse in a prespecified cortical target. This can be used to transiently disrupt the function of the targeted cortical region and explore causal relations to behavior, assess cortical reactivity, and map out functionally relevant brain regions, for example during presurgical assessments. Particularly when applied repetitively, TMS can modify cortical excitability and the effects can propagate trans-synaptically to interconnected cortical, subcortical, and spinal cord regions. As such, TMS can be used to assess the functional integrity of neural circuits and to modulate brain activity with potential therapeutic intent.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen D, Cuffin BN. Developing a more focal magnetic stimulator: part I: some basic principles. J Clin Neurophysiol 1991;8:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Roth BJ, Cohen LG, Hallett M, et al. A theoretical calculation of the electric field induced by magnetic stimulation of a peripheral nerve. Muscle Nerve 1990;13:734–741. - PubMed
-
- Hallett M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a primer. Neuron 2007:55:187–199. - PubMed
-
- Amassian VE, Stewart M, Quirk GJ, et al. Physiological basis of motor effects of a transient stimulus to cerebral cortex. Neurosurgery 1987:20:74–93. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
