Substituted 2-phenylimidazopyridines: a new class of drug leads for human African trypanosomiasis
- PMID: 24354316
- PMCID: PMC3962778
- DOI: 10.1021/jm401178t
Substituted 2-phenylimidazopyridines: a new class of drug leads for human African trypanosomiasis
Abstract
A phenotypic screen of a compound library for antiparasitic activity on Trypanosoma brucei, the causative agent of human African trypanosomiasis, led to the identification of substituted 2-(3-aminophenyl)oxazolopyridines as a starting point for hit-to-lead medicinal chemistry. A total of 110 analogues were prepared, which led to the identification of 64, a substituted 2-(3-aminophenyl)imidazopyridine. This compound showed antiparasitic activity in vitro with an EC50 of 2 nM and displayed reasonable druglike properties when tested in a number of in vitro assays. The compound was orally bioavailable and displayed good plasma and brain exposure in mice. Compound 64 cured mice infected with Trypanosoma brucei when dosed orally down to 2.5 mg/kg. Given its potent antiparasitic properties and its ease of synthesis, compound 64 represents a new lead for the development of drugs to treat human African trypanosomiasis.
Figures
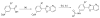
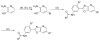
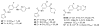
References
-
- Lutje V, Seixas J, Kennedy A. Chemotherapy for second-stage human African trypanosomiasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010:CD006201. - PubMed
-
- Brun R, Don R, Jacobs RT, Wang MZ, Barrett MP. Development of novel drugs for African trypanosomiasis. Future Microbiol. 2011;6:677–791. - PubMed
-
- Harstad TW, Little BB, Bawdon RE, Knoll K, Roe D, Gilstrap LC. Pharmacokinetics of pentamidine in Sprague-Dawley rats in late pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1990;163:912–916. - PubMed
-
- Freeman SJ, Lloyd JB. Evidence that suramin and aurothiomalate are teratogenic in rat by disturbing yolk sac-mediated embryonic protein nutrition. Chem Biol Interact. 1986;58:149–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

