Endovascular treatment of traumatic carotid cavernous fistula with balloon-assisted sinus coiling. A technical description and initial results
- PMID: 24355148
- PMCID: PMC3902743
- DOI: 10.1177/159101991301900407
Endovascular treatment of traumatic carotid cavernous fistula with balloon-assisted sinus coiling. A technical description and initial results
Abstract
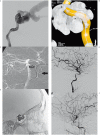
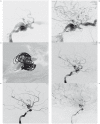
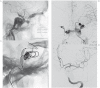
This study aimed to propose an alternative treatment for carotid cavernous fistula (CCF) using the balloon-assisted sinus coiling (BASC) technique and to describe this procedure in detail. Under general anesthesia, we performed the BASC procedure to treat five patients with traumatic CCF. Percutaneous access was obtained via the right femoral artery, and a 7F sheath was inserted, or alternatively, a bifemoral 6F approach was accomplished. A microcatheter was inserted into the cavernous sinus over a 0.014-inch microwire through the fistulous point; the microcatheter was placed distal from the fistula point, and a "U-turn" maneuver was performed. Through the same carotid access, a compliant balloon was advanced to cross the point of the fistula and cover the whole carotid tear. Large coils were inserted using the microcatheter in the cavernous sinus. Coils filled the adjacent cavernous sinus, respecting the balloon. Immediate complete angiographic resolution was achieved, and an early angiographic control (mean = 2.6 months) indicated complete stability without recanalization. The clinical follow-up has been uneventful without any recurrence (mean = 15.2 months). An endovascular approach is optimal for direct CCF. Because the detachable balloon has been withdrawn from the market, covered stenting requires antiplatelet therapy and its patency is unconfirmed, but cavernous sinus coiling remains an excellent treatment option. Currently, there is no detailed description of the BASC procedure. We provide detailed angiograms with suitable descriptions of the exact fistula point, and venous drainage pathways. Familiarity with these devices makes this technique effective, easy and safe.
Keywords: carotid artery; cavernous sinus fistula; embolization; endovascular treatment; trauma.
Figures
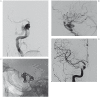
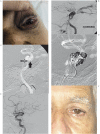
References
-
- Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, et al. Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid- cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg. 985;62:248–256. - PubMed
-
- Elhammady MS, Peterson EC, Aziz-Sultan MA. Onyx embolization of a carotid cavernous fistula via direct transorbital puncture. J Neurosurg. 2011;114(1):129–132. - PubMed
-
- Gemmete JJ, Chaudhary N, Pandey A, et al. Treatment of carotid cavernous fistulas. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2010;12(1):43–53. - PubMed
-
- Serbinenko FA. Balloon catheterization and occlusion of major cerebral vessels. J Neurosurg. 1974;41:25–145. - PubMed
-
- Goto K, Hieshima GB, Higashida RT, et al. Treatment of direct carotid cavernous sinus fistulae. Various therapeutic approaches and results in 148 cases. Acta Radiol Suppl. 1986;369:576–579. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

