Bilateral cervical spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas with intracranial venous drainage mimicking a foramen magnum dural arteriovenous fistula
- PMID: 24355154
- PMCID: PMC3902749
- DOI: 10.1177/159101991301900413
Bilateral cervical spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas with intracranial venous drainage mimicking a foramen magnum dural arteriovenous fistula
Abstract
We describe a unique case of bilateral cervical spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas mimicking an intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula near the foramen magnum. We review its detection via MRI and digital subtraction angiography and subsequent management through surgical intervention. Pitfalls in diagnostic angiography are discussed with reference to accurate location of the fistula site. The venous anastomotic connections of the posterior midline spinal vein to the medial posterior medullary vein, posterior fossa bridging veins, and dural venous sinuses of the skull base are discussed with reference to problem-solving in this complex case. The mechanism of myelopathy through venous hypertension produced by spinal dural fistulas is also emphasized.
Keywords: MR angiography; MR imaging; digital subtraction angiography; spinal angiography; spinal dural arteriovenous fistula; spine; vascular malformations.
Figures
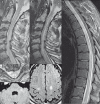


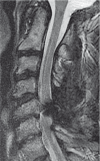
References
-
- Narvid J, Hetts SW, Larsen D, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: clinical features and long-term results. Neurosurgery. 2008;62:159–166. discussion 166-157. - PubMed
-
- Hetts SW, Moftakhar P, English JD, et al. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas and intrathecal venous drainage: correlation between digital subtraction angiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and clinical findings. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Oshita J, Yamaguchi S, Ohba S, et al. Mirror-image spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas at the craniocervical junction: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2011;69:E1166–1171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

