Synthesis and molecular modeling of six novel monastrol analogues: evaluation of cytotoxicity and kinesin inhibitory activity against HeLa cell line
- PMID: 24355209
- PMCID: PMC3891991
- DOI: 10.1186/2008-2231-21-70
Synthesis and molecular modeling of six novel monastrol analogues: evaluation of cytotoxicity and kinesin inhibitory activity against HeLa cell line
Abstract
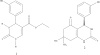
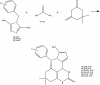
Background and the purpose of the study: A common approach in cancer chemotherapy is development of drugs that interrupt the mitosis phase of cell division. Dimethylenastron is a known kinesin inhibitor. In this study, six novel dimethylenastron analogues (4a-f), in which 3-hydroxyphenyl substituent has been replaced with substituted benzylimidazolyl, were synthesized through Biginelli reaction.
Methods: Six novel Biginelli compounds (4a-f) were synthesized through one step Biginelli reaction of imidazole aldehydes (3a-c), dimedone and urea or thioura. In vitro cytotoxicities of prepared compounds were investigated using MTT assay. Furthermore the ELIPA kit was implemented to study inhibitory effects of synthesized compounds on ATPase activity of kinesin by measuring of organic phosphate.
Results: Our results indicated that analogue 4c is the most toxic and analogues 4f, 4b and dimethylenasteron were less cytotoxic in compare with other analogues. On the other hand, analogue 4a, 4b, 4c and 4e showed stronger Kinesin inhibition as compared with analogue 4f and dimethylenasteron. None of synthesized compounds were as potent kinesin inhibitor as Taxol. Docking analysis revealed that hydrogen bond formation and hydrophobic interactions were the key factors affecting inhibitory effects of these compounds.
Conclusion: Newly synthesized compounds were found to have moderate to good cytotoxicity against HeLa cancer cell. Our results may be helpful in further design of dihydropyrimidine as potential anticancer agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel Dihydropyrimidinones Synthesized through Modified Biginelli Reaction as Eg5 Kinesin Inhibitors with Potential Anti-cancer Effects: In vitro and In vivo Studies.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025 Apr 30. doi: 10.2174/0118715206373183250324063523. Online ahead of print. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40325529
-
Monastrol mimic Biginelli dihydropyrimidinone derivatives: synthesis, cytotoxicity screening against HepG2 and HeLa cell lines and molecular modeling study.Org Med Chem Lett. 2012 Jun 12;2(1):23. doi: 10.1186/2191-2858-2-23. Org Med Chem Lett. 2012. PMID: 22691177 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of β-Enaminonitrile-Linked 8-Methoxy-1H-Benzo[f]Chromene Moieties and Analysis of Their Antitumor Mechanisms.Front Chem. 2021 Nov 22;9:759148. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.759148. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34881224 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and molecular docking study of new monastrol analogues as kinesin spindle protein inhibitors.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020 Aug;353(8):e2000060. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202000060. Epub 2020 May 26. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2020. PMID: 32452567
-
Cephalostatin analogues--synthesis and biological activity.Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 2004;87:1-80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-0581-8_1. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 2004. PMID: 15079895 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin(thio)one Containing Scaffold: Biginelli-like Reactions.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;15(8):948. doi: 10.3390/ph15080948. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, cytotoxic assessment, and molecular docking studies of 2,6-diaryl-substituted pyridine and 3,4- dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-one scaffolds.Turk J Chem. 2020 Feb 11;44(1):194-213. doi: 10.3906/kim-1903-72. eCollection 2020. Turk J Chem. 2020. PMID: 33488152 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic Poisons in Research and Medicine.Molecules. 2020 Oct 12;25(20):4632. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204632. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33053667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monastrol derivatives: in silico and in vitro cytotoxicity assessments.Res Pharm Sci. 2020 Jul 3;15(3):249-262. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.288427. eCollection 2020 Jun. Res Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33088325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verweij J, Clavel M, Chevalier B. Paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere): not simply two of a kind. Ann Oncol. 1994;21:495–505. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

