Rapid and simultaneous quantitation of prostanoids by UPLC-MS/MS in rat brain
- PMID: 24355215
- PMCID: PMC4134920
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.11.041
Rapid and simultaneous quantitation of prostanoids by UPLC-MS/MS in rat brain
Abstract
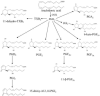
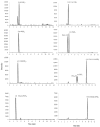
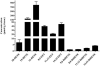
The metabolites of arachidonic acid (AA) produced from the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway, collectively termed as prostanoids, and from the CYP 450 pathway, eicosanoids, have been implicated in various neuro-degenerative and neuroinflammatory diseases. This study developed a quantitative UPLC-MS/MS method to simultaneously measure 11 prostanoids including prostaglandins and cyclopentenone metabolites in the rat brain cortical tissue. Linear calibration curves ranging from 0.104 to 33.3ng/ml were validated. The inter-day and intra-day variance for all metabolites was less than 15%. The extraction recovery efficiency and matrix (deionized water) effects measured at 12.5ng/ml (750pg on column) ranged from 88 to 100% and 3 to 14%, respectively, with CV% values below 20%. Additionally, applying the processing and extraction conditions of this method to our previous CYP450 eicosanoids method resulted in overall improvement in extraction recovery and reduction in matrix effects at low (0.417ng/ml) and high (8.33ng/ml) concentrations. In rat brain cortical tissue samples, concentrations of prostanoids ranged from 10.2 to 937pmol/g wet tissue and concentration of eicosanoids ranged from 2.23 to 793pmol/g wet tissue. These data demonstrate that the successive measurement of prostanoids and eicosanoids from a single extracted sample of rat brain tissue can be achieved with a UPLC-MS/MS system and that this method is necessary for evaluation of these metabolites to delineate their role in various neuroinflammatory and cerebrovascular disorders.
Keywords: AA; Arachidonic acid; COX; CV; CYP450; Cyclooxygenase; DiHETE; EET; Eicosanoids; HETE; Ischemic stroke; PG; Prostanoids; QC; SPE; UPLC–MS/MS; arachidonic acid; coefficient of variation; cyclooxygenase; cytochrome P450; dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid; epoxyeicosatrienoic acid; hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; prostaglandins; quality control; solid phase extraction; ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
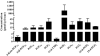
References
-
- Gryglewski RJ. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Akaike A, Kaneko S, Tamura Y, Nakata N, Shiomi H, Ushikubi F, Narumiya S. Brain research. 1994;663:237–243. - PubMed
-
- Takadera T, Yumoto H, Tozuka Y, Ohyashiki T. Neurosci Lett. 2002;317:61–64. - PubMed
-
- Liu D, Wu L, Breyer R, Mattson MP, Andreasson K. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:758–761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

