Dietary fibre intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24355537
- PMCID: PMC3898422
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f6879
Dietary fibre intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To investigate dietary fibre intake and any potential dose-response association with coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease.
Design: Systematic review of available literature and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort studies using random effects models.
Data sources: The Cochrane Library, Medline, Medline in-process, Embase, CAB Abstracts, ISI Web of Science, BIOSIS, and hand searching.
Eligibility criteria for studies: Prospective studies reporting associations between fibre intake and coronary heart disease or cardiovascular disease, with a minimum follow-up of three years and published in English between 1 January 1990 and 6 August 2013.
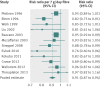
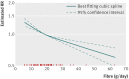
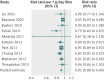
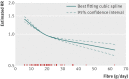
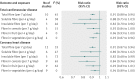
Results: 22 cohort study publications met inclusion criteria and reported total dietary fibre intake, fibre subtypes, or fibre from food sources and primary events of cardiovascular disease or coronary heart disease. Total dietary fibre intake was inversely associated with risk of cardiovascular disease (risk ratio 0.91 per 7 g/day (95% confidence intervals 0.88 to 0.94)) and coronary heart disease (0.91 (0.87 to 0.94)). There was evidence of some heterogeneity between pooled studies for cardiovascular disease (I(2)=45% (0% to 74%)) and coronary heart disease (I(2)=33% (0% to 66%)). Insoluble fibre and fibre from cereal and vegetable sources were inversely associated with risk of coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease. Fruit fibre intake was inversely associated with risk of cardiovascular disease.
Conclusions: Greater dietary fibre intake is associated with a lower risk of both cardiovascular disease and coronary heart disease. Findings are aligned with general recommendations to increase fibre intake. The differing strengths of association by fibre type or source highlight the need for a better understanding of the mode of action of fibre components.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures
References
-
- Allender S, Scarborough P, Peto V, Rayner M, Leal J, Luengo-Fernandez R, et al. European cardiovascular disease statistics. 2008. www.bhf.org.uk/publications/view-publication.aspx?ps=1001443.
-
- Unal B, Critchley JA, Capewell S. Explaining the decline in coronary heart disease mortality in England and Wales between 1981 and 2000. Circulation 2004;109:1101-7. - PubMed
-
- Trowell H. Ischemic heart disease and dietary fiber. Am J Clin Nutr 1972;25:926-32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
