Angiotensin II-dependent TGF-β signaling contributes to Loeys-Dietz syndrome vascular pathogenesis
- PMID: 24355923
- PMCID: PMC3871227
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI69666
Angiotensin II-dependent TGF-β signaling contributes to Loeys-Dietz syndrome vascular pathogenesis
Abstract
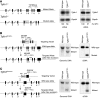
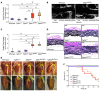
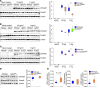
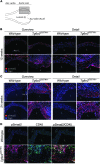
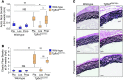
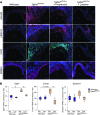
Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) is a connective tissue disorder that is characterized by a high risk for aneurysm and dissection throughout the arterial tree and phenotypically resembles Marfan syndrome. LDS is caused by heterozygous missense mutations in either TGF-β receptor gene (TGFBR1 or TGFBR2), which are predicted to result in diminished TGF-β signaling; however, aortic surgical samples from patients show evidence of paradoxically increased TGF-β signaling. We generated 2 knockin mouse strains with LDS mutations in either Tgfbr1 or Tgfbr2 and a transgenic mouse overexpressing mutant Tgfbr2. Knockin and transgenic mice, but not haploinsufficient animals, recapitulated the LDS phenotype. While heterozygous mutant cells had diminished signaling in response to exogenous TGF-β in vitro, they maintained normal levels of Smad2 phosphorylation under steady-state culture conditions, suggesting a chronic compensation. Analysis of TGF-β signaling in the aortic wall in vivo revealed progressive upregulation of Smad2 phosphorylation and TGF-β target gene output, which paralleled worsening of aneurysm pathology and coincided with upregulation of TGF-β1 ligand expression. Importantly, suppression of Smad2 phosphorylation and TGF-β1 expression correlated with the therapeutic efficacy of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist losartan. Together, these data suggest that increased TGF-β signaling contributes to postnatal aneurysm progression in LDS.
Figures


Comment in
-
Aortic aneurysms in Loeys-Dietz syndrome - a tale of two pathways?J Clin Invest. 2014 Jan;124(1):79-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI73906. Epub 2013 Dec 20. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24355917 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

