Predicting the glomerular filtration rate in bariatric surgery patients
- PMID: 24356416
- PMCID: PMC3945154
- DOI: 10.1159/000357231
Predicting the glomerular filtration rate in bariatric surgery patients
Abstract
Background/aims: Identifying the best method to estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in bariatric surgery patients has important implications for the clinical care of obese patients and research into the impact of obesity and weight reduction on kidney health. We therefore performed such an analysis in patients before and after surgical weight loss.
Methods: Fasting measured GFR (mGFR) by plasma iohexol clearance before and after bariatric surgery was obtained in 36 severely obese individuals. Estimated GFR was calculated using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation, the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation using serum creatinine only, the CKD-EPI equation using serum cystatin C only and a recently derived equation that uses both serum creatinine and cystatin C (CKD-EPIcreat-cystC) and then compared to mGFR.
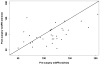
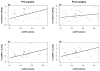
Results: Participants were primarily middle-aged white females with a mean baseline body mass index of 46 ± 9, serum creatinine of 0.81 ± 0.24 mg/dl and mGFR of 117 ± 40 ml/min. mGFR had a stronger linear relationship with inverse cystatin C before (r = 0.28, p = 0.09) and after (r = 0.38, p = 0.02) surgery compared to the inverse of creatinine (before: r = 0.26, p = 0.13; after: r = 0.11, p = 0.51). mGFR fell by 17 ± 35 ml/min (p = 0.007) following surgery. The CKD-EPIcreat-cystC was unquestionably the best overall performing estimating equation before and after surgery, revealing very little bias and a capacity to estimate mGFR within 30% of its true value over 80% of the time. This was true whether or not mGFR was indexed for body surface area.
Conclusions: In severely obese bariatric surgery patients with normal kidney function, cystatin C is more strongly associated with mGFR than is serum creatinine. The CKD-EPIcreat-cystC equation best predicted mGFR both before and after surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflict of interest to report
Figures
References
-
- Ezzati M, Riboli E. Behavioral and dietary risk factors for noncommunicable diseases. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:954–964. - PubMed
-
- Friedman A. Implications and management of obesity in kidney disease. In: Byham-Gray L, Burrows J, Chertow G, editors. Nutrition in kidney disease. NY, NY: Springer Publishing; in press.
-
- Neff KJ, Frankel AH, Tam FW, Sadlier DM, Godson C, le Roux CW. The effect of bariatric surgery on renal function and disease: A focus on outcomes and inflammation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical