The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: overview
- PMID: 24356592
- PMCID: PMC3867999
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-2112
The diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study at 30 years: overview
Abstract
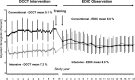
OBJECTIVE The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) was designed to test the glucose hypothesis and determine whether the complications of type 1 diabetes (T1DM) could be prevented or delayed. The Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) observational follow-up determined the durability of the DCCT effects on the more-advanced stages of diabetes complications including cardiovascular disease (CVD). RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS The DCCT (1982-1993) was a controlled clinical trial in 1,441 subjects with T1DM comparing intensive therapy (INT), aimed at achieving levels of glycemia as close to the nondiabetic range as safely possible, with conventional therapy (CON), which aimed to maintain safe asymptomatic glucose control. INT utilized three or more daily insulin injections or insulin pump therapy guided by self-monitored glucose. EDIC (1994-present) is an observational study of the DCCT cohort. RESULTS The DCCT followed >99% of the cohort for a mean of 6.5 years and demonstrated a 35-76% reduction in the early stages of microvascular disease with INT, with a median HbA1c of 7%, compared with CONV, with a median HbA1c of 9%. The major adverse effect of INT was a threefold increased risk of hypoglycemia, which was not associated with a decline in cognitive function or quality of life. EDIC showed a durable effect of initial assigned therapies despite a loss of the glycemic separation (metabolic memory) and demonstrated that the reduction in early-stage complications during the DCCT translated into substantial reductions in severe complications and CVD. CONCLUSIONS DCCT/EDIC has demonstrated the effectiveness of INT in reducing the long-term complications of T1DM and improving the prospects for a healthy life span.
Figures

References
-
- Banting FG, Best CH. The internal secretion of the pancreas: 1922. Indian J Med Res 2007;125:251–266 - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;328:1676–1685 - PubMed
-
- Deckert T, Poulsen JE, Larsen M. Prognosis of diabetes with diabetes onset before the age of thirty-one. Diabetologia 1978;14:363–377 - PubMed
-
- Siperstein MD, Foster DW, Knowles HC, Jr, Levine R, Madison LL, Roth J. Control of blood glucose and diabetic vascular disease. N Engl J Med 1977;296:1060–1063 - PubMed
-
- Boyd JD, Jackson RL, Allen JH. Avoidance of degenerative lesions in diabetes mellitus. JAMA 1942;118:694
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

