Update on cardiovascular outcomes at 30 years of the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study
- PMID: 24356596
- PMCID: PMC3868002
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-2116
Update on cardiovascular outcomes at 30 years of the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study
Abstract
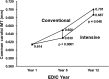
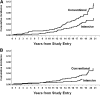
OBJECTIVE To describe the beneficial long-term effects of an average of 6.5 years of intensive diabetes therapy (INT) in type 1 diabetes on measures of atherosclerosis, cardiac structure and function, and clinical cardiovascular events observed in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) and the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS The DCCT was a randomized clinical trial of 1,441 participants assigned to receive INT or conventional therapy (CON). It was conducted between 1983-1993 with an average follow-up of 6.5 years. EDIC (1994-present) is an observational follow-up of the DCCT cohort. Cardiovascular events have been recorded throughout. During EDIC common carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) was measured with ultrasound, coronary artery calcification with computed tomography, and cardiac structure and function with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. RESULTS DCCT INT and lower levels of HbA1c during DCCT/EDIC were associated with thinner carotid IMT, less coronary calcification, and a lower incidence of clinical cardiovascular events including myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiac death. While there were no significant differences in cardiac structure and function between the former INT and CON groups, they were significantly associated with higher HbA1c during DCCT/EDIC. CONCLUSIONS DCCT INT and the attendant 6.5 years of lower HbA1c had long-term salutary effects on the development and progression of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease during the subsequent follow-up during EDIC.
Figures
References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–986 - PubMed
-
- Lachin J, Genuth S, Nathan D, Davis M, The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group Retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes four years after a trial of intensive therapy. N Engl J Med 2000;342:381–389 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lachin JM, Genuth S, Nathan DM, Zinman B, Rutledge BN, DCCT/EDIC Research Group Effect of glycemic exposure on the risk of microvascular complications in the diabetes control and complications trial—revisited. Diabetes 2008;57:995–1001 - PubMed
-
- Writing Team for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group Sustained effect of intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus on development and progression of diabetic nephropathy: the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study. JAMA 2003;290:2159–2167 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orchard TJ, Costacou T, Kretowski A, Nesto RW. Type 1 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2528–2538 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

