Outcomes of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma that do not meet eligibility criteria for clinical trials
- PMID: 24356626
- PMCID: PMC4155479
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdt492
Outcomes of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma that do not meet eligibility criteria for clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Targeted therapies in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) have been approved based on registration clinical trials that have strict eligibility criteria. The clinical outcomes of patients treated with targeted agents but are ineligible for trials are unknown.
Patients and methods: mRCC patients treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy were retrospectively deemed ineligible for clinical trials (according to commonly used inclusion/exclusion criteria) if they had a Karnofsky performance status (KPS) <70%, nonclear-cell histology, brain metastases, hemoglobin ≤9 g/dl, creatinine >2× the upper limit of normal, corrected calcium ≥12 mg/dl, platelet count of <100 × 10(3)/uL, or neutrophil count <1500/mm(3).
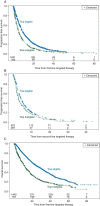
Results: Overall, 768 of 2210 (35%) patients in the International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) were deemed ineligible for clinical trials by the above criteria. Between ineligible versus eligible patients, the response rate, median progression-free survival (PFS) and median overall survival of first-line targeted therapy were 22% versus 29% (P = 0.0005), 5.2 versus 8.6 months, and 12.5 versus 28.4 months (both P < 0.0001), respectively. Second-line PFS (if applicable) was 2.8 months in the trial ineligible versus 4.3 months in the trial eligible patients (P = 0.0039). When adjusted by the IMDC prognostic categories, the HR for death between trial ineligible and trial eligible patients was 1.55 (95% confidence interval 1.378-1.751, P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: The number of patients that are ineligible for clinical trials is substantial and their outcomes are inferior. Specific trials addressing the unmet needs of protocol ineligible patients are warranted.
Keywords: clinical trials; ineligible; metastatic renal cell cancer; outcomes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SWITCH: A Randomised, Sequential, Open-label Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Sorafenib-sunitinib Versus Sunitinib-sorafenib in the Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer.Eur Urol. 2015 Nov;68(5):837-47. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 May 4. Eur Urol. 2015. PMID: 25952317 Clinical Trial.
-
Risk factors and model for predicting toxicity-related treatment discontinuation in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy: Results from the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium.Cancer. 2016 Feb 1;122(3):411-9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.29773. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26540173
-
Sequential targeted therapy after pazopanib therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer: efficacy and toxicity.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2014 Aug;12(4):262-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24795159
-
Targeted therapies and complete responses in first line treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. A meta-analysis of published trials.Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 Mar;40(2):271-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 24070900 Review.
-
[Value of targeted therapies for renal cell cancer].Urologe A. 2008 Oct;47(10):1303-10. doi: 10.1007/s00120-008-1746-x. Urologe A. 2008. PMID: 18587556 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma patients: real-world experience in Japan.Int J Clin Oncol. 2024 Dec;29(12):1931-1936. doi: 10.1007/s10147-024-02633-w. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39472358
-
Pazopanib in Metastatic Renal Cancer: A "Real-World" Experience at National Cancer Institute "Fondazione G. Pascale".Front Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 31;7:287. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00287. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27630568 Free PMC article.
-
Use of record linkage to evaluate treatment outcomes and trial eligibility in a real-world metastatic prostate cancer population in Scotland.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2020 Jun;29(6):653-663. doi: 10.1002/pds.4998. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2020. PMID: 32316077 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Axitinib After Nivolumab Failure in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.In Vivo. 2020 May-Jun;34(3):1541-1546. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11943. In Vivo. 2020. PMID: 32354960 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of efficacy and safety of sorafenib in kidney cancer patients aged 75 years and older: a propensity score-matched analysis.Br J Cancer. 2018 Jul;119(2):241-247. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0129-3. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29891937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:125–134. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B, Bellmunt J, Negrier S, et al. Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (AVOREN): final analysis of overall survival. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2144–2150. - PubMed
-
- Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2271–2281. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

