Parameningeal rhabdomyosarcoma in pediatric age: results of a pooled analysis from North American and European cooperative groups
- PMID: 24356633
- PMCID: PMC3868324
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdt426
Parameningeal rhabdomyosarcoma in pediatric age: results of a pooled analysis from North American and European cooperative groups
Erratum in
- Ann Oncol. 2014 Mar;25(3):756
-
Parameningeal rhabdomyosarcoma in pediatric age: results of a pooled analysis from North American and European cooperative groups.Ann Oncol. 2014 Mar;25(3):756. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu001. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Ann Oncol. 2014. PMID: 32664045 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Parameningeal (PM) site is a well-known adverse prognostic factor in children with localized rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS). To identify risk factors associated with outcome at this site, we pooled data from 1105 patients treated in 10 studies conducted by European and North American cooperative groups between 1984 and 2004.
Patients and methods: Clinical factors including age, histology, size, invasiveness, nodal involvement, Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study (IRS) clinical group, site, risk factors for meningeal involvement (MI), study group, and application of radiotherapy (RT) were studied for their impact on event-free and overall survival (EFS and OS).
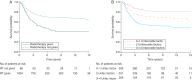
Results: Ten-year EFS and OS were 62.6 and 66.1% for the whole group. Patients without initial RT showed worse survival (10-year OS 40.8% versus 68.5% for RT treated patients). Multivariate analysis focusing on 862 patients who received RT as part of their initial treatment revealed four unfavorable prognostic factors: age <3 or >10 years, signs of MI, unfavorable site, and tumor size. Utilizing these prognostic factors, patients could be classified into different risk groups with 10-year OS ranging between 51.1 and 80.9%.
Conclusions: While, in general, PM localization is regarded as an adverse prognostic factor, the current analysis differentiates those with good prognosis (36% patients with 0-1 risk factor: 10-year OS 80.9%) from high-risk PM patients (28% with 3-4 factors: 10-year OS 51.1%). Furthermore, this analysis reinforces the necessity for RT in PM RMS.
Keywords: meningeal involvement; parameningeal; radiotherapy; rhabdomyosarcoma.
Figures
References
-
- Miller RW, Young JL, Jr, Novakovic B. Childhood cancer. Cancer. 1995;75:395–405. - PubMed
-
- Arndt CA, Stoner JA, Hawkins DS, et al. Vincristine, actinomycin, and cyclophosphamide compared with vincristine, actinomycin, and cyclophosphamide alternating with vincristine, topotecan, and cyclophosphamide for intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma: Children's Oncology Group study D9803. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5182–5188. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dantonello TM, Int-Veen C, Harms D, et al. Cooperative trial CWS-91 for localized soft tissue sarcoma in children, adolescents, and young adults. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1446–1455. - PubMed
-
- Oberlin O, Rey A, Sanchez de Toledo J, et al. Randomized comparison of intensified six-drug versus standard three-drug chemotherapy for high-risk nonmetastatic rhabdomyosarcoma and other chemotherapy-sensitive childhood soft tissue sarcomas: long-term results from the International Society of Pediatric Oncology MMT95 study. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2457–2465. - PubMed
-
- Raney RB, Meza J, Anderson JR, et al. Treatment of children and adolescents with localized parameningeal sarcoma: experience of the Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group protocols IRS-II through -IV, 1978–1997. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2002;38:22–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases