β-cell dedifferentiation in diabetes is important, but what is it?
- PMID: 24356710
- PMCID: PMC4010577
- DOI: 10.4161/isl.27494
β-cell dedifferentiation in diabetes is important, but what is it?
Abstract
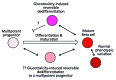
This commentary discusses the concept of β-cell dedifferentiation in diabetes, which is important but not well defined. A broad interpretation is that a state of differentiation has been lost, which means changes in gene expression as well as in structural and functional elements. Thus, a fully mature healthy β cell will have its unique differentiation characteristics, but maturing cells and old β cells will have different patterns of gene expression and might therefore be considered as dedifferentiated. The meaning of dedifferentiation is now being debated because β cells in the diabetic state lose components of their differentiated state, which results in severe dysfunction of insulin secretion. The major cause of this change is thought to be glucose toxicity (glucotoxicity) and that lowering glucose levels with treatment results in some restoration of function. An issue to be discussed is whether dedifferentiated β cells return to a multipotent precursor cell phenotype or whether they follow a different pathway of dedifferentiation.
Keywords: dedifferentiation; diabetes; differentiation; insulin secretion; islets; β cell.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of β-cell dedifferentiation in diabetes: recent findings and future research directions.J Endocrinol. 2018 Feb;236(2):R109-R143. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0516. Epub 2017 Dec 4. J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29203573 Review.
-
Evidence of β-Cell Dedifferentiation in Human Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Mar;101(3):1044-54. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2860. Epub 2015 Dec 29. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26713822 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of β-cell identity and dedifferentiation, not an irreversible process?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 10;15:1414447. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1414447. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38915897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noradrenergic fibers are associated with beta-cell dedifferentiation and impaired beta-cell function in humans.Metabolism. 2021 Jan;114:154414. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154414. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Metabolism. 2021. PMID: 33129839
-
Induction of α cell-restricted Gc in dedifferentiating β cells contributes to stress-induced β-cell dysfunction.JCI Insight. 2019 May 23;5(13):e128351. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.128351. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31120862 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Eugenol in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Macrophages and Its Role in Preventing β-Cell Dedifferentiation and Loss Induced by High Glucose-High Lipid Conditions.Molecules. 2023 Nov 16;28(22):7619. doi: 10.3390/molecules28227619. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38005341 Free PMC article.
-
β-cell dysfunction: Its critical role in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes.World J Diabetes. 2015 Feb 15;6(1):109-24. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109. World J Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25685282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 Overexpression Induces β-Cell Dysfunction and Increases Beta-cell Susceptibility to Damage.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 3;290(27):16772-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.642041. Epub 2015 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25971976 Free PMC article.
-
A Brief Review of the Mechanisms of β-Cell Dedifferentiation in Type 2 Diabetes.Nutrients. 2021 May 10;13(5):1593. doi: 10.3390/nu13051593. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34068827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Polycomb-Dependent Epigenome Controls β Cell Dysfunction, Dedifferentiation, and Diabetes.Cell Metab. 2018 Jun 5;27(6):1294-1308.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.04.013. Epub 2018 May 10. Cell Metab. 2018. PMID: 29754954 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
