Fenretinide induces ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase in human retinal pigment epithelial cells
- PMID: 24357007
- PMCID: PMC3999186
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24527
Fenretinide induces ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase in human retinal pigment epithelial cells
Abstract
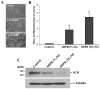
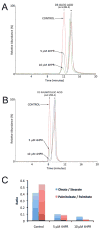
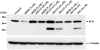
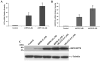
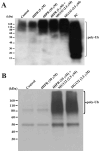
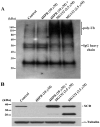
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD, SCD1), an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) resident protein and a rate-limiting enzyme in monounsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis, regulates cellular functions by controlling the ratio of saturated to monounsaturated fatty acids. Increase in SCD expression is strongly implicated in the proliferation and survival of cancer cells, whereas its decrease is known to impair proliferation, induce apoptosis, and restore insulin sensitivity. We examined whether fenretinide, (N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide, 4HPR), which induces apoptosis in cancer cells and recently shown to improve insulin sensitivity, can modulate the expression of SCD. We observed that fenretinide decreased SCD protein and enzymatic activity in the ARPE-19 human retinal pigment epithelial cell line. Increased expression of BiP/GRP78, ATF4, and GADD153 implicated ER stress. Tunicamycin and thapsigargin, compounds known to induce ER stress, also decreased the SCD protein. This decrease was completely blocked by the proteasome inhibitor MG132. In addition, PYR41, an inhibitor of ubiquitin activating enzyme E1, blocked the fenretinide-mediated decrease in SCD. Immunoprecipitation analysis using anti-ubiquitin and anti-SCD antibodies and the blocking of SCD loss by PYR41 inhibition of ubiquitination further corroborate that fenretinide mediates the degradation of SCD in human RPE cells via the ubiquitin-proteasome dependent pathway. Therefore, the effect of fenretinide on SCD should be considered in its potential therapeutic role against cancer, type-2 diabetes, and retinal diseases.
© 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Acharya P, Engel JC, Correia MA. Hepatic CYP3A suppression by high concentrations of proteasomal inhibitors: a consequence of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress induction, activation of RNA-dependent protein kinase-like ER-bound eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha (eIF2alpha)-kinase (PERK) and general control nonderepressible-2 eIF2alpha kinase (GCN2), and global translational shutoff. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;76:503–515. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Camerini T, Mariani L, De Palo G, Marubini E, Di Mauro MG, Decensi A, Costa A, Veronesi U. Safety of the synthetic retinoid fenretinide: long-term results from a controlled clinical trial for the prevention of contralateral breast cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2001;19:1664–1670. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Sun X, Ran Q, Wilkinson KD, Murphy TJ, Simons JW, Dong JT. Ubiquitin-proteasome degradation of KLF5 transcription factor in cancer and untransformed epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2005;24:3319–3327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

