Serial femtosecond crystallography of G protein-coupled receptors
- PMID: 24357322
- PMCID: PMC3902108
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1244142
Serial femtosecond crystallography of G protein-coupled receptors
Abstract
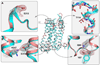
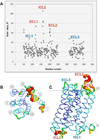
X-ray crystallography of G protein-coupled receptors and other membrane proteins is hampered by difficulties associated with growing sufficiently large crystals that withstand radiation damage and yield high-resolution data at synchrotron sources. We used an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) with individual 50-femtosecond-duration x-ray pulses to minimize radiation damage and obtained a high-resolution room-temperature structure of a human serotonin receptor using sub-10-micrometer microcrystals grown in a membrane mimetic matrix known as lipidic cubic phase. Compared with the structure solved by using traditional microcrystallography from cryo-cooled crystals of about two orders of magnitude larger volume, the room-temperature XFEL structure displays a distinct distribution of thermal motions and conformations of residues that likely more accurately represent the receptor structure and dynamics in a cellular environment.
Figures
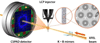
Comment in
-
Making protein crystals fly.Nat Methods. 2014 Apr;11(4):366-7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2913. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 24818225 No abstract available.
-
Serial femtosecond crystallography datasets from G protein-coupled receptors.Sci Data. 2016 Aug 1;3:160057. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2016.57. Sci Data. 2016. PMID: 27479354 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

