Sexual function, activity, and satisfaction among women receiving maintenance hemodialysis
- PMID: 24357510
- PMCID: PMC3878703
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05470513
Sexual function, activity, and satisfaction among women receiving maintenance hemodialysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Past studies that demonstrated that sexual dysfunction is common among women receiving chronic hemodialysis did not distinguish sexual dysfunction/difficulty from sexual inactivity. This study sought to differentiate these in order to elucidate the prevalence of true "sexual dysfunction" in this population.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: As part of a clinical trial of symptom management strategies in patients receiving chronic hemodialysis, female sexual function was prospectively assessed monthly for 6 months and quarterly thereafter using the Female Sexual Function Index, to which questions were added differentiating sexual dysfunction/difficulty from sexual inactivity. Beginning in month 7, patients were asked three questions about sexual activity, difficulty, and satisfaction monthly.
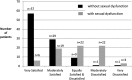
Results: Of the women enrolled in the clinical trial,125 participants completed 1721 assessments between 2009 and 2011. Scores on 574 of 643 (89%) quarterly Female Sexual Function Index assessments were consistent with sexual dysfunction, due largely to sexual inactivity, which was reported on 525 (82%) quarterly assessments. When reported (n=1663), the most frequently described reasons for sexual inactivity were lack of interest in sex (n=715; 43%) and lack of a partner (n=647; 39%), but rarely sexual difficulty (n=36; 2%). When reported (n=1582), women were moderately to very satisfied with their sexual life on 1020 (64%) assessments and on 513 of 671 (76%) assessments in which lack of interest was cited as a reason for sexual inactivity. Women indicated an interest in learning about the causes of and treatment for sexual dysfunction on just 5% of all assessments.
Conclusions: Although many women receiving chronic hemodialysis are sexually inactive, few describe sexual difficulty. Most, including those with a lack of interest in sex, are satisfied with their sexual life and few wish to learn about treatment options. These findings suggest that true sexual dysfunction is uncommon in this population and that treatment opportunities are rare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Sexual Inactivity among hemodialysis patients: the patients' perspective.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Jan;9(1):6-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11831113. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24357511 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kimmel PL, Emont SL, Newmann JM, Danko H, Moss AH: ESRD patient quality of life: Symptoms, spiritual beliefs, psychosocial factors, and ethnicity. Am J Kidney Dis 42: 713–721, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Kimmel PL, Patel SS: Quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: Focus on end-stage renal disease treated with hemodialysis. Semin Nephrol 26: 68–79, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Kimmel PL, Peterson RA: Depression in end-stage renal disease patients treated with hemodialysis: Tools, correlates, outcomes, and needs. Semin Dial 18: 91–97, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Merkus MP, Jager KJ, Dekker FW, de Haan RJ, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT: Physical symptoms and quality of life in patients on chronic dialysis: Results of The Netherlands Cooperative Study on Adequacy of Dialysis (NECOSAD). Nephrol Dial Transplant 14: 1163–1170, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Rosas SE, Joffe M, Franklin E, Strom BL, Kotzker W, Brensinger C, Grossman E, Glasser DB, Feldman HI: Association of decreased quality of life and erectile dysfunction in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 64: 232–238, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous