It's like a juggling act: rheumatoid arthritis patient perspectives on daily life and flare while on current treatment regimes
- PMID: 24357813
- PMCID: PMC3970565
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket416
It's like a juggling act: rheumatoid arthritis patient perspectives on daily life and flare while on current treatment regimes
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to explore patients' experiences of RA daily life while on modern treatments.
Methods: The methods of this study comprised semi-structured interviews with 15 RA patients, analysed using inductive thematic analysis.
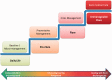
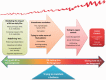
Results: Four themes suggest patients experience life with RA along a continuum from RA in the background to the foreground of their lives, underpinned by constant actions to maintain balance. Living with RA in the background shows patients experience continuous, daily symptoms, which they mediate through micromanagement (mediating the impact of RA on daily life), while learning to incorporate RA into their identity (redefining me). RA moving into the foreground shows patients experience fluctuating symptoms (unwelcome reminders) that may or may not lead to a flare (trying to make sense of fluctuation). Dealing with RA in the foreground shows how patients attempt to manage RA flares (trying to regain control) and decide to seek medical help only after feeling they are losing control. Patients employ a stepped approach to self-management (mediation ladder) as symptoms increase, with seeking medical help often seen as the last resort. Patients seek to find a balance between managing their fluctuating RA and living their daily lives.
Conclusion: Patients move back and forth along a continuum of RA in the background vs the foreground by balancing self-management of symptoms and everyday life. Clinicians need to appreciate that daily micromanagement is needed, even on current treatment regimes. Further research is needed to quantify the level and impact of daily symptoms and identify barriers and facilitators to seeking help.
Keywords: daily life; flare; help-seeking; impact; interviews; qualitative; rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Hill J. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1998. Rheumatology Nursing: A Creative Approach.
-
- Newman S, Fitzpatrick R, Revenson TA, et al. London: Routledge; 1995. Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis.
-
- Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, et al. A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness. Health Technol Assess. 2006;10:1–266. - PubMed
-
- Maxwell LJ, Singh JA. Abatacept for rheumatoid arthritis: a Cochrane systematic review. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:234–45. - PubMed
-
- Stenström CH, Bergman B, Dahlgren LO. Everyday life with rheumatoid arthritis: a phenomenographic study. Physiother Theory Pract. 1993;9:235–43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical