Changes in Cortical Activity During Real and Imagined Movements: an ERP Study
- PMID: 24358049
- PMCID: PMC3866622
- DOI: 10.2174/1745017901309010196
Changes in Cortical Activity During Real and Imagined Movements: an ERP Study
Abstract
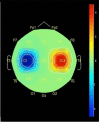
This study aims to compare the topographic distribution of cortical activation between real and imagined movement through event-related potential (ERP). We are specifically interested in identifying, the topographic distribution of activated areas, the intensity of activated areas, and the temporal occurrence of these activations on preparation and motor response phases. Twelve healthy and right handed subjects were instructed to perform a task under real and imagery conditions. The task was performed simultaneously to electroencephalographic (EEG) recording. When compared the conditions, we found a statistically significant difference in favor of real condition revealed by performing an unpaired t-test with multiple corrections of Bonferroni, demonstrating negative activity on electrode C3 and positive activity on the electrode C4 only in motor response phase. These findings revealed similar functional connections established during real and imagery conditions, suggesting that there are common neural substrate and similar properties of functional integration shared by conditions.
Keywords: Cortical activity; ERP; event-related potential; imagined and real movements..
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of cortical connectivity during real and imagined rhythmic finger tapping.Brain Topogr. 2007 Spring;19(3):137-45. doi: 10.1007/s10548-007-0020-7. Brain Topogr. 2007. PMID: 17587169
-
Functional Equivalence of Imagined vs. Real Performance of an Inhibitory Task: An EEG/ERP Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2016 Sep 16;10:467. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00467. eCollection 2016. Front Hum Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27695410 Free PMC article.
-
Low-frequency neural activity at rest is correlated with the movement-related cortical potentials elicited during both real and imagined movements.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Jan 18;742:135530. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135530. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33248162
-
Neural processes mediating the preparation and release of focal motor output are suppressed or absent during imagined movement.Exp Brain Res. 2015 May;233(5):1625-37. doi: 10.1007/s00221-015-4237-5. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Exp Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25744055 Free PMC article.
-
ERD/ERS patterns reflecting sensorimotor activation and deactivation.Prog Brain Res. 2006;159:211-22. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)59014-4. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17071233 Review.
Cited by
-
The dissociation between command following and communication in disorders of consciousness: an fMRI study in healthy subjects.Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Sep 15;9:493. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00493. eCollection 2015. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26441593 Free PMC article.
-
The Power of Faith: The Influence of Athletes' Coping Self-Efficacy on the Cognitive Processing of Psychological Stress.Front Psychol. 2019 Jul 11;10:1565. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01565. eCollection 2019. Front Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31354577 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Lasting Cortical Reorganization as the Result of Motor Imagery of Throwing a Ball in a Virtual Tennis Court.Front Psychol. 2015 Dec 1;6:1869. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01869. eCollection 2015. Front Psychol. 2015. PMID: 26648903 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of motor imagery on the learning of a fine hand motor skill.Exp Brain Res. 2017 Jan;235(1):305-320. doi: 10.1007/s00221-016-4794-2. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Exp Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 27714404
References
-
- Jeannerod M. The representing brain neural correlates of motor intention and imagery. Brain Behav Sci. 1994;17:187–245.
-
- Jeannerod M. Mental imagery in the motor context. Neuropsychologia. 1995;33:1419–32. - PubMed
-
- Jeannerod M. Neural simulation of action a unifying mechanism for motor cognition. NeuroImage. 2001;14:103–9. - PubMed
-
- Decety J, Grezes J. Neural mechanisms subserving the perception of human actions. Trends Cogn Sci. 1999;3:172–8. - PubMed
-
- Jackson PL, Doyon J, Richards CL, Malouin F. Potential role of mental practice using motor imagery in neurological rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82:1133–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous