C-terminal domain of ICA69 interacts with PICK1 and acts on trafficking of PICK1-PKCα complex and cerebellar plasticity
- PMID: 24358315
- PMCID: PMC3865253
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083862
C-terminal domain of ICA69 interacts with PICK1 and acts on trafficking of PICK1-PKCα complex and cerebellar plasticity
Abstract
Background: PICK1 (protein interacting with C-kinase 1) is a PKC (protein kinase C)-binding protein, which is essential for synaptic plasticity. The trafficking of PKCα-PICK1 complex to plasma membrane is critical for the internalization of GluR2 and induction of long-term depression. ICA69 (islet cell autoantigen 69 kDa) is identified as a major binding partner of PICK1. While heteromeric BAR domain complex is suggested to underlie the interaction between PICK1 and ICA69, the role of C-terminal domain of ICA69 (ICAC) in PICK1-ICA69 complex is unknown.
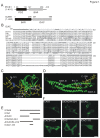
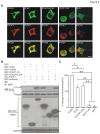
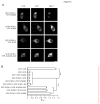
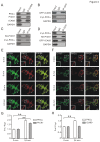
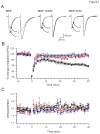
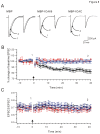
Methodology/principal findings: We found that ICAC interacted with PICK1 and regulated the trafficking of PICK1-PKCα complex. ICAC and ΔICAC (containing BAR domain) might function distinctly in the association of ICA69 with PICK1. While ΔICAC domain inclined to form clusters, the distribution of ICAC was diffuse. The trafficking of PICK1 to plasma membrane mediated by activated PKCα was inhibited by ICA69. This action might ascribe to ICAC, because overexpression of ICAC, but not ΔICAC, interrupted PKCα-mediated PICK1 trafficking. Notably, infusion of maltose binding protein (MBP) fusion protein, MBP-ICA69 or MBP-ICAC, in cerebellar Purkinje cells significantly inhibited the induction of long-term depression at parallel fiber- and climbing fiber-Purkinje cell synapses.
Conclusions: Our experiments showed that ICAC is an important domain for the ICA69-PICK1 interaction and plays essential roles in PICK1-mediated neuronal plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
PICK1-ICA69 heteromeric BAR domain complex regulates synaptic targeting and surface expression of AMPA receptors.J Neurosci. 2007 Nov 21;27(47):12945-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2040-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18032668 Free PMC article.
-
Islet-cell autoantigen 69 mediates the antihyperalgesic effects of electroacupuncture on inflammatory pain by regulating spinal glutamate receptor subunit 2 phosphorylation through protein interacting with C-kinase 1 in mice.Pain. 2019 Mar;160(3):712-723. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001450. Pain. 2019. PMID: 30699097 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid binding regulates synaptic targeting of PICK1, AMPA receptor trafficking, and synaptic plasticity.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 1;26(9):2380-90. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3503-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16510715 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of PICK1.Neurosignals. 2006-2007;15(4):190-201. doi: 10.1159/000098482. Epub 2007 Jan 11. Neurosignals. 2006. PMID: 17215589 Review.
-
Multiple faces of protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1): Structure, function, and diseases.Neurochem Int. 2016 Sep;98:115-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 26970394 Review.
Cited by
-
AMPA receptors and their minions: auxiliary proteins in AMPA receptor trafficking.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jun;76(11):2133-2169. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03068-7. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30937469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase C regulates AMPA receptor auxiliary protein Shisa9/CKAMP44 through interactions with neuronal scaffold PICK1.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Aug 15;7(9):1234-1245. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12261. eCollection 2017 Sep. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 28904854 Free PMC article.
-
ICA1 affects APP processing through the PICK1-PKCα signaling pathway.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jun;30(6):e14754. doi: 10.1111/cns.14754. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38884369 Free PMC article.
-
ICA69 regulates activity-dependent synaptic strengthening and learning and memory.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 May 12;16:1171432. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1171432. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37251649 Free PMC article.
-
Rod bipolar cells dysfunction occurs before ganglion cells loss in excitotoxin-damaged mouse retina.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Dec 2;10(12):905. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2140-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31787761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iwakura Y, Nagano T, Kawamura M, Horikawa H, Ibaraki K et al. (2001) N-Methyl-D-aspartate-induced alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazoleproprionic acid (AMPA) receptor down-regulation involves interaction of the carboxyl terminus of GluR2/3 with Pick1. Ligand-binding studies using Sindbis vectors carrying AMPA receptor decoys. J Biol Chem 276: 40025-40032. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103125200. PubMed: 11498531. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

