Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte-enterocyte crosstalk regulates production of bactericidal angiogenin 4 by Paneth cells upon microbial challenge
- PMID: 24358364
- PMCID: PMC3866140
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084553
Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte-enterocyte crosstalk regulates production of bactericidal angiogenin 4 by Paneth cells upon microbial challenge
Abstract
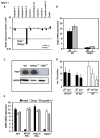
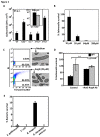
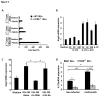
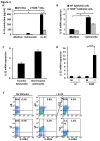
Antimicrobial proteins influence intestinal microbial ecology and limit proliferation of pathogens, yet the regulation of their expression has only been partially elucidated. Here, we have identified a putative pathway involving epithelial cells and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (iIELs) that leads to antimicrobial protein (AMP) production by Paneth cells. Mice lacking γδ iIELs (TCRδ(-/-)) express significantly reduced levels of the AMP angiogenin 4 (Ang4). These mice were also unable to up-regulate Ang4 production following oral challenge by Salmonella, leading to higher levels of mucosal invasion compared to their wild type counterparts during the first 2 hours post-challenge. The transfer of γδ iIELs from wild type (WT) mice to TCRδ(-/-) mice restored Ang4 production and Salmonella invasion levels were reduced to those obtained in WT mice. The ability to restore Ang4 production in TCRδ(-/-) mice was shown to be restricted to γδ iIELs expressing Vγ7-encoded TCRs. Using a novel intestinal crypt co-culture system we identified a putative pathway of Ang4 production initiated by exposure to Salmonella, intestinal commensals or microbial antigens that induced intestinal epithelial cells to produce cytokines including IL‑23 in a TLR-mediated manner. Exposure of TCR-Vγ7(+) γδ iIELs to IL-23 promoted IL‑22 production, which triggered Paneth cells to secrete Ang4. These findings identify a novel role for γδ iIELs in mucosal defence through sensing immediate epithelial cell cytokine responses and influencing AMP production. This in turn can contribute to the maintenance of intestinal microbial homeostasis and epithelial barrier function, and limit pathogen invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intraepithelial gammadelta+ lymphocytes maintain the integrity of intestinal epithelial tight junctions in response to infection.Gastroenterology. 2006 Sep;131(3):818-29. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.06.003. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 16952551
-
γδ Intraepithelial Lymphocyte Migration Limits Transepithelial Pathogen Invasion and Systemic Disease in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2015 Jun;148(7):1417-26. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.02.053. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25747597 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and intercompartmental movement of gammadelta T cells: intestinal intraepithelial and peripheral gammadelta T cells represent exclusive nonoverlapping populations with distinct migration characteristics.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 1;185(9):5160-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001652. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20870939
-
Development of TCR gamma delta iIELs.Semin Immunol. 1995 Oct;7(5):299-305. doi: 10.1016/1044-5323(95)90011-x. Semin Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8580462 Review.
-
[Molecular biological characterization of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes and their receptors].Nihon Rinsho. 1996 Apr;54(4):1162-9. Nihon Rinsho. 1996. PMID: 8920691 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Ribonuclease A Superfamily in Humans: Canonical RNases as the Buttress of Innate Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 5;17(8):1278. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081278. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27527162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial HNF4A shapes the intraepithelial lymphocyte compartment via direct regulation of immune signaling molecules.J Exp Med. 2022 Aug 1;219(8):e20212563. doi: 10.1084/jem.20212563. Epub 2022 Jul 6. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35792863 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of host-derived molecules that interact with gut microbiota.Imeta. 2023 Feb 13;2(2):e88. doi: 10.1002/imt2.88. eCollection 2023 May. Imeta. 2023. PMID: 38868433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maintenance of Barrier Tissue Integrity by Unconventional Lymphocytes.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 14;12:670471. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.670471. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33936115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual function of angiogenin-4 inducing intestinal stem cells and apoptosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Nov 2;11:1181145. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1181145. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38020881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson CL, Ouellete AJ, Satchell DP, Ayabe T, Lopez-Boado YS et al. (1999) Regulation of intestinal α-defensin activation by the metalloproteinase matrilysin in innate host defence. Science 286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

