Rho associated coiled-coil kinase-1 regulates collagen-induced phosphatidylserine exposure in platelets
- PMID: 24358370
- PMCID: PMC3865301
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084649
Rho associated coiled-coil kinase-1 regulates collagen-induced phosphatidylserine exposure in platelets
Abstract
Background: The transbilayer movement of phosphatidylserine mediates the platelet procoagulant activity during collagen stimulation. The Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y-27632 inhibits senescence induced but not activation induced phosphatidylserine exposure. To investigate further the specific mechanisms, we now utilized mice with genetic deletion of the ROCK1 isoform.
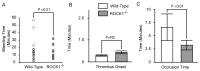
Methods and results: ROCK1-deficient mouse platelets expose significantly more phosphatidylserine and generate more thrombin upon activation with collagen compared to wild-type platelets. There were no significant defects in platelet shape change, aggregation, or calcium response compared to wild-type platelets. Collagen-stimulated ROCK1-deficient platelets also displayed decreased phosphorylation levels of Lim Kinase-1 and cofilin-1. However, there was no reduction in phosphorylation levels of myosin phosphatase subunit-1 (MYPT1) or myosin light chain (MLC). In an in vivo light/dye-induced endothelial injury/thrombosis model, ROCK1-deficient mice presented a shorter occlusion time in cremasteric venules when compared to wild-type littermates (3.16 ± 1.33 min versus 6.6 ± 2.6 min; p = 0.01).
Conclusions: These studies define ROCK1 as a new regulator for collagen-induced phosphatidylserine exposure in platelets with functional consequences on thrombosis. This effect was downstream of calcium signaling and was mediated by Lim Kinase-1 / cofilin-1-induced cytoskeletal changes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Platelet shape change is mediated by both calcium-dependent and -independent signaling pathways. Role of p160 Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase in platelet shape change.J Biol Chem. 1999 Oct 1;274(40):28293-300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.40.28293. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10497186
-
Amyloid β peptide stimulates platelet activation through RhoA-dependent modulation of actomyosin organization.FASEB J. 2014 Apr;28(4):1819-29. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-243691. Epub 2014 Jan 13. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24421399
-
Platelet senescence and phosphatidylserine exposure.Transfusion. 2010 Oct;50(10):2167-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2010.02676.x. Epub 2010 Oct 4. Transfusion. 2010. PMID: 20456701 Free PMC article.
-
Organized migration of epithelial cells requires control of adhesion and protrusion through Rho kinase effectors.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Mar;292(3):G806-17. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00333.2006. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17138966
-
Role of Rho kinases in abnormal and normal hematopoiesis.Curr Opin Hematol. 2014 Jul;21(4):271-5. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000056. Curr Opin Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24867289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wdr1-Dependent Actin Reorganization in Platelet Activation.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 14;11(9):e0162897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162897. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27627652 Free PMC article.
-
RAP1-RHO small GTPase cross-talk mediates integrin-dependent and -independent platelet procoagulant response.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 23:2025.05.22.655614. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.22.655614. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40475636 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The plasma membrane calcium pump: new ways to look at an old enzyme.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 11;289(15):10261-10268. doi: 10.1074/jbc.O114.555565. Epub 2014 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24570005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rac1 Modulates Endothelial Function and Platelet Aggregation in Diabetes Mellitus.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Apr 6;7(8):e007322. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007322. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29626150 Free PMC article.
-
Trpc6 gain-of-function disease mutation enhances phosphatidylserine exposure in murine platelets.PLoS One. 2022 Jun 24;17(6):e0270431. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270431. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35749414 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

