Alternative Non-Antibody Protein Scaffolds for Molecular Imaging of Cancer
- PMID: 24358455
- PMCID: PMC3863941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coche.2013.08.009
Alternative Non-Antibody Protein Scaffolds for Molecular Imaging of Cancer
Abstract
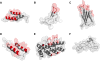
The development of improved methods for early detection and characterization of cancer presents a major clinical challenge. One approach that has shown excellent potential in preclinical and clinical evaluation is molecular imaging with small-scaffold, non-antibody based, engineered proteins. These novel diagnostic agents produce high contrast images due to their fast clearance from the bloodstream and healthy tissues, can be evolved to bind a multitude of cancer biomarkers, and are easily functionalized by site-specific bioconjugation methods. Several small protein scaffolds have been verified for in vivo molecular imaging including affibodies and their two-helix variants, knottins, fibronectins, DARPins, and several natural ligands. Further, the biodistribution of these engineered ligands can be optimized through rational mutation of the conserved regions, careful selection and placement of chelator, and modification of molecular size.
Figures
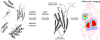
References
-
- Schmidt MM, Wittrup KD. A modeling analysis of the effects of molecular size and binding affinity on tumor targeting. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2861–2871. A mechanistic mathematical model is developed and validated to predict the impact of molecular size and binding affinity on delivery to tumors. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schottelius M, Wester HJ. Molecular imaging targeting peptide receptors. Methods. 2009;48:161–177. - PubMed
-
- Feldwisch J, Tolmachev V. Engineering of affibody molecules for therapy and diagnostics. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;899:103–126. - PubMed
-
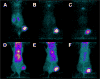
- Orlova A, Magnusson M, Eriksson TLJ, Nilsson M, Larsson B, Höidén-Guthenberg I, Widström C, Carlsson J, Tolmachev V, Ståhl S, et al. Tumor imaging using a picomolar affinity HER2 binding affibody molecule. Cancer Res. 2006;66:4339–4348. An affibody, evolved to 22 pM affinity for HER2 and radiolabeled with 125I, exhibited excellent tumor targeting capabilities in a subcutaneously xenografted tumor model in mice as measured by excised tissue biodistribution and gamma scintigraphy. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
