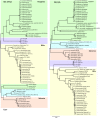
Streptococcal taxonomy based on genome sequence analyses
- PMID: 24358875
- PMCID: PMC3799547
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.2-67.v1
Streptococcal taxonomy based on genome sequence analyses
Abstract
The identification of the clinically relevant viridans streptococci group, at species level, is still problematic. The aim of this study was to extract taxonomic information from the complete genome sequences of 67 streptococci, comprising 19 species, by means of genomic analyses, multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA), average amino acid identity (AAI), genomic signatures, genome-to-genome distances (GGD) and codon usage bias. We then attempted to determine the usefulness of these genomic tools for species identification in streptococci. Our results showed that MLSA, AAI and GGD analyses are robust markers to identify streptococci at the species level, for instance, S. pneumoniae, S. mitis, and S. oralis. A Streptococcus species can be defined as a group of strains that share ≥ 95% DNA similarity in MLSA and AAI, and > 70% DNA identity in GGD. This approach allows an advanced understanding of bacterial diversity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM: Taxonomic Note: A place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S ribosomal-RNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1994;44(4):846–849 10.1099/00207713-44-4-846 - DOI
-
- Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, et al. : Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1987;37(4):463–464 10.1099/00207713-37-4-463 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources