Rapid and pervasive changes in genome-wide enhancer usage during mammalian development
- PMID: 24360275
- PMCID: PMC3989111
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.033
Rapid and pervasive changes in genome-wide enhancer usage during mammalian development
Abstract
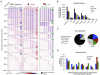
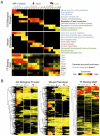
Enhancers are distal regulatory elements that can activate tissue-specific gene expression and are abundant throughout mammalian genomes. Although substantial progress has been made toward genome-wide annotation of mammalian enhancers, their temporal activity patterns and global contributions in the context of developmental in vivo processes remain poorly explored. Here we used epigenomic profiling for H3K27ac, a mark of active enhancers, coupled to transgenic mouse assays to examine the genome-wide utilization of enhancers in three different mouse tissues across seven developmental stages. The majority of the ∼90,000 enhancers identified exhibited tightly temporally restricted predicted activity windows and were associated with stage-specific biological functions and regulatory pathways in individual tissues. Comparative genomic analysis revealed that evolutionary conservation of enhancers decreases following midgestation across all tissues examined. The dynamic enhancer activities uncovered in this study illuminate rapid and pervasive temporal in vivo changes in enhancer usage that underlie processes central to development and disease.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Akamatsu W, Okano HJ, Osumi N, Inoue T, Nakamura S, Sakakibara S, Miura M, Matsuo N, Darnell RB, Okano H. Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.a. 1999;96:9885–9890. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Austin CP, Cepko CL. Cellular migration patterns in the developing mouse cerebral cortex. Development. 1990;110:713–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 HG003988/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE020060/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034661/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS062859A/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM105202/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM105202/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37MH049428/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG003988/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS062859/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH049428/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01DE020060/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS099099/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081880/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

