Mutations in CSPP1 lead to classical Joubert syndrome
- PMID: 24360807
- PMCID: PMC3882909
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.11.015
Mutations in CSPP1 lead to classical Joubert syndrome
Abstract
Joubert syndrome and related disorders (JSRDs) are genetically heterogeneous and characterized by a distinctive mid-hindbrain malformation. Causative mutations lead to primary cilia dysfunction, which often results in variable involvement of other organs such as the liver, retina, and kidney. We identified predicted null mutations in CSPP1 in six individuals affected by classical JSRDs. CSPP1 encodes a protein localized to centrosomes and spindle poles, as well as to the primary cilium. Despite the known interaction between CSPP1 and nephronophthisis-associated proteins, none of the affected individuals in our cohort presented with kidney disease, and further, screening of a large cohort of individuals with nephronophthisis demonstrated no mutations. CSPP1 is broadly expressed in neural tissue, and its encoded protein localizes to the primary cilium in an in vitro model of human neurogenesis. Here, we show abrogated protein levels and ciliogenesis in affected fibroblasts. Our data thus suggest that CSPP1 is involved in neural-specific functions of primary cilia.
Copyright © 2014 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
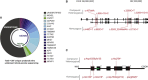
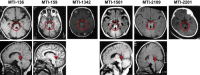
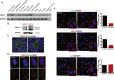
References
-
- Maria B.L., Hoang K.B., Tusa R.J., Mancuso A.A., Hamed L.M., Quisling R.G., Hove M.T., Fennell E.B., Booth-Jones M., Ringdahl D.M. “Joubert syndrome” revisited: key ocular motor signs with magnetic resonance imaging correlation. J. Child Neurol. 1997;12:423–430. - PubMed
-
- Valente E.M., Brancati F., Dallapiccola B. Genotypes and phenotypes of Joubert syndrome and related disorders. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2008;51:1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- DK068306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK068306/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01HD070494/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS048453/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079310/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018521/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS041537/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052455/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD070494/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS041537/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS052455/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

