The N-terminal methionine of cellular proteins as a degradation signal
- PMID: 24361105
- PMCID: PMC3988316
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.031
The N-terminal methionine of cellular proteins as a degradation signal
Abstract
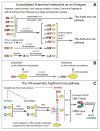
The Arg/N-end rule pathway targets for degradation proteins that bear specific unacetylated N-terminal residues while the Ac/N-end rule pathway targets proteins through their N(α)-terminally acetylated (Nt-acetylated) residues. Here, we show that Ubr1, the ubiquitin ligase of the Arg/N-end rule pathway, recognizes unacetylated N-terminal methionine if it is followed by a hydrophobic residue. This capability of Ubr1 expands the range of substrates that can be targeted for degradation by the Arg/N-end rule pathway because virtually all nascent cellular proteins bear N-terminal methionine. We identified Msn4, Sry1, Arl3, and Pre5 as examples of normal or misfolded proteins that can be destroyed through the recognition of their unacetylated N-terminal methionine. Inasmuch as proteins bearing the Nt-acetylated N-terminal methionine residue are substrates of the Ac/N-end rule pathway, the resulting complementarity of the Arg/N-end rule and Ac/N-end rule pathways enables the elimination of protein substrates regardless of acetylation state of N-terminal methionine in these substrates.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






Comment in
-
Crosstalk between the Arg/N-end and Ac/N-end rule.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(9):1366-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.28751. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24698805 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arnesen T, Van Damme P, Polevoda B, Helsens K, Evjenth R, Colaert N, Varhaug JE, Vandekerckhove J, Lillehaug JR, Sherman F, et al. Proteomics analyses reveal the evolutionary conservation and divergence of N-terminal acetyltransferases from yeast to humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:8157–8162. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachmair A, Finley D, Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986;234:179–186. - PubMed
-
- Behnia R, Panic B, Whyte JRC, Munro S. Targeting of the Arf-like GTPase Arl3p to the Golgi requires N-terminal acetylation and the membrane protein Sys1p. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Choi WS, Jeong BC, Joo YJ, Lee MR, Kim J, Eck MJ, Song HK. Structural basis for the recognition of N-end rule substrates by the UBR box of ubiquitin ligases. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17:1175–1181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

