(13)C-labelled microdialysis studies of cerebral metabolism in TBI patients
- PMID: 24361470
- PMCID: PMC4013834
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.12.012
(13)C-labelled microdialysis studies of cerebral metabolism in TBI patients
Abstract
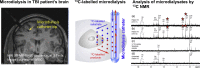
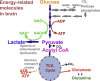
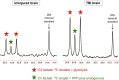
Human brain chemistry is incompletely understood and better methodologies are needed. Traumatic brain injury (TBI) causes metabolic perturbations, one result of which includes increased brain lactate levels. Attention has largely focussed on glycolysis, whereby glucose is converted to pyruvate and lactate, and is proposed to act as an energy source by feeding into neurons' tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, generating ATP. Also reportedly upregulated by TBI is the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) that does not generate ATP but produces various molecules that are putatively neuroprotective, antioxidant and reparative, in addition to lactate among the end products. We have developed a novel combination of (13)C-labelled cerebral microdialysis both to deliver (13)C-labelled substrates into brains of TBI patients and recover the (13)C-labelled metabolites, with high-resolution (13)C NMR analysis of the microdialysates. This methodology has enabled us to achieve the first direct demonstration in humans that the brain can utilise lactate via the TCA cycle. We are currently using this methodology to make the first direct comparison of glycolysis and the PPP in human brain. In this article, we consider the application of (13)C-labelled cerebral microdialysis for studying brain energy metabolism in patients. We set this methodology within the context of metabolic pathways in the brain, and (13)C research modalities addressing them.
Keywords: (13)C-labelling; Brain metabolism; Human; Microdialysis; NMR; Traumatic brain injury.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Andrew E.R., Bradbury A., Eades R.G. Removal of dipolar broadening of nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of solids by specimen rotation. Nature. 1959;183:1802–1803.
-
- Antoniewicz M.R. Tandem mass spectrometry for measuring stable-isotope labeling. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013;24:48–53. - PubMed
-
- Bartnik B.L., Sutton R.L., Fukushima M., Harris N.G., Hovda D.A., Lee S.M. Upregulation of pentose phosphate pathway and preservation of tricarboxylic acid cycle flux after experimental brain injury. J. Neurotrauma. 2005;22:1052–1065. - PubMed
-
- Bartnik B.L., Lee S.M., Hovda D.A., Sutton R.L. The fate of glucose during the period of decreased metabolism after fluid percussion injury: a 13C NMR study. J. Neurotrauma. 2007;24:1079–1092. - PubMed
-
- Bellander B.M., Cantais E., Enblad P., Hutchinson P., Nordstrom C.H., Robertson C., Sahuquillo J., Smith M., Stocchetti N., Ungerstedt U., Unterberg A., Olsen N.V. Consensus meeting on microdialysis in neurointensive care. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:2166–2169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0001354/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600986/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- G1002277/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HTA/13/15/02/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MC_U105663142/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600986 ID 79068/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- NIHR-RP-R3-12-013/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- G1002277 ID 98489/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9439390 ID 65883/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9439390/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

