CD4+ T cells and IFN-γ are required for the development of Pneumocystis-associated pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 24361497
- PMCID: PMC3906492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.10.027
CD4+ T cells and IFN-γ are required for the development of Pneumocystis-associated pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
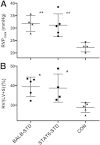
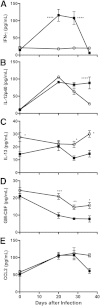
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a disease of diverse etiology. Although primary PH can develop in the absence of prior disease, PH more commonly develops in conjunction with other pulmonary pathologies. We previously reported a mouse model in which PH occurs as a sequela of Pneumocystis infection in the context of transient CD4 depletion. Here, we report that instead of the expected Th2 pathways, the Th1 cytokine IFN-γ is essential for the development of PH, as wild-type mice developed PH but IFN-γ knockout mice did not. Because gene expression analysis showed few strain differences that were not immune-function related, we focused on those responses as potential pathologic mechanisms. In addition to dependence on IFN-γ, we found that when CD4 cells were continuously depleted, but infection was limited by antibiotic treatment, PH did not occur, confirming that CD4 T cells are required for PH development. Also, although CD8 T-cells are implicated in the pathology of Pneumocystis pneumonia, they did not have a role in the onset of PH. Finally, we found differences in immune cell phenotypes that correlated with PH, including elevated CD204 expression in lung CD11c(+) cells, but their role remains unclear. Overall, we demonstrate that a transient, localized, immune response requiring IFN-γ and CD4-T cells can disrupt pulmonary vascular function and promote lingering PH.
Copyright © 2014 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Simonneau G., Robbins I.M., Beghetti M., Channick R.N., Delcroix M., Denton C.P., Elliott C.G., Gaine S.P., Gladwin M.T., Jing Z.C., Krowka M.J., Langleben D., Nakanishi N., Souza R. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(1 Suppl):S43–S54. - PubMed
-
- Pullamsetti S.S., Savai R., Janssen W., Dahal B.K., Seeger W., Grimminger F., Ghofrani H.A., Weissmann N., Schermuly R.T. Inflammation, immunological reaction and role of infection in pulmonary hypertension. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011;17:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Voelkel N.F., Tuder R.M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of severe pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 1995;8:2129–2138. - PubMed
-
- Tuder R.M., Voelkel N.F. Pulmonary hypertension and inflammation. J Lab Clin Med. 1998;132:16–24. - PubMed
-
- Larsen K.O., Yndestad A., Sjaastad I., Løberg E.M., Goverud I.L., Halvorsen B., Jia J., Andreassen A.K., Husberg C., Jonasson S., Lipp M., Christensen G., Aukrust P., Skjønsberg O.H. Lack of CCR7 induces pulmonary hypertension involving perivascular leukocyte infiltration and inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011;301:L50–L59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

