Treatment as long-term prevention: sustained reduction in HIV sexual transmission risk with use of antiretroviral therapy in rural Uganda
- PMID: 24361683
- PMCID: PMC4038415
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000136
Treatment as long-term prevention: sustained reduction in HIV sexual transmission risk with use of antiretroviral therapy in rural Uganda
Abstract
Objectives: Suppressive antiretroviral therapy (ART) substantially decreases HIV transmission in clinical research settings. We sought to measure the frequency and correlates of periods of transmission risk among individuals taking ART during multiple years of observation in rural, southwestern Uganda.
Design: Observational cohort study.
Methods: We collected sexual behavior and viral load data in a Ugandan cohort of people living with HIV/AIDS from the time of ART initiation. We defined each 90-day visit as a potential transmission period if HIV-1 RNA was more than 400 copies/ml and the participant reported sexual transmission risk behavior, defined as unprotected sexual contact with at least 1 HIV-uninfected partners or partners of unknown serostatus in the prior 90 days.
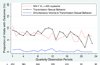
Results: We evaluated data from 463 individuals on ART over a median 3.5 years of observation and 5293 total study visits. During that time, over half (259, 56%) had detectable viremia or reported sexual transmission risk behavior at least once. However, only 23 (5%) had both simultaneously, at 28 (<1%) of all visits. Transmission sexual behavior was reported at 6% of visits with detectable viremia. In multivariable regression modeling, correlates of transmission risk periods included younger age, lower CD4 cell count, low household asset ownership and increased internalized stigma.
Conclusion: Although detectable viremia and/or sexual transmission risk behavior occurred in over half of individuals, ART reduced periods of HIV transmission risk by over 90% during up to 6 years of observation time. These findings provide further support for provision of ART, along with interventions to promote long-term adherence, to reduce HIV transmission in HIV-endemic settings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in sexual behavior and risk of HIV transmission after antiretroviral therapy and prevention interventions in rural Uganda.AIDS. 2006 Jan 2;20(1):85-92. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000196566.40702.28. AIDS. 2006. PMID: 16327323
-
HIV Transmission Risk Persists During the First 6 Months of Antiretroviral Therapy.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2016 Aug 15;72(5):579-84. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001019. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2016. PMID: 27070123 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual behavior and HIV transmission risk of Ugandan adults taking antiretroviral therapy: 3 year follow-up.AIDS. 2011 Jun 19;25(10):1317-27. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e328347f775. AIDS. 2011. PMID: 21522005
-
Screening for HIV Infection in Asymptomatic, Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force.JAMA. 2019 Jun 18;321(23):2337-2348. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.2592. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31184705
-
The risk of sexual transmission of HIV in individuals with low-level HIV viraemia: a systematic review.Lancet. 2023 Aug 5;402(10400):464-471. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00877-2. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Lancet. 2023. PMID: 37490935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship Dynamics and Partner Beliefs About Viral Suppression: A Longitudinal Study of Male Couples Living with HIV/AIDS (The Duo Project).AIDS Behav. 2016 Jul;20(7):1572-83. doi: 10.1007/s10461-016-1423-9. AIDS Behav. 2016. PMID: 27150895 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Risk Behaviors of Patients with HIV/AIDS over the Course of Antiretroviral Treatment in Northern Vietnam.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 May 29;15(6):1106. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15061106. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29844289 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in CD4 count at presentation to care and treatment initiation in sub-Saharan Africa, 2002-2013: a meta-analysis.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Apr 1;60(7):1120-7. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu1137. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25516189 Free PMC article.
-
Reclaiming fertility awareness methods to inform timed intercourse for HIV serodiscordant couples attempting to conceive.J Int AIDS Soc. 2015 Jan 9;18(1):19447. doi: 10.7448/IAS.18.1.19447. eCollection 2015. J Int AIDS Soc. 2015. PMID: 25579801 Free PMC article.
-
Intimacy versus isolation: a qualitative study of sexual practices among sexually active HIV-infected patients in HIV care in Brazil, Thailand, and Zambia.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 20;10(3):e0120957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120957. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25793283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attia S, Egger M, Muller M, Zwahlen M, Low N. Sexual transmission of HIV according to viral load and antiretroviral therapy: systematic review and meta-analysis. AIDS. 2009;23:1397–1404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23MH079713/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23MH087228/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23MH096620/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH054907/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH079713/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH087227/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K24MH087227/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH096620/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30AI27763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH054907 AND/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH099916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH087228/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23MH099916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

